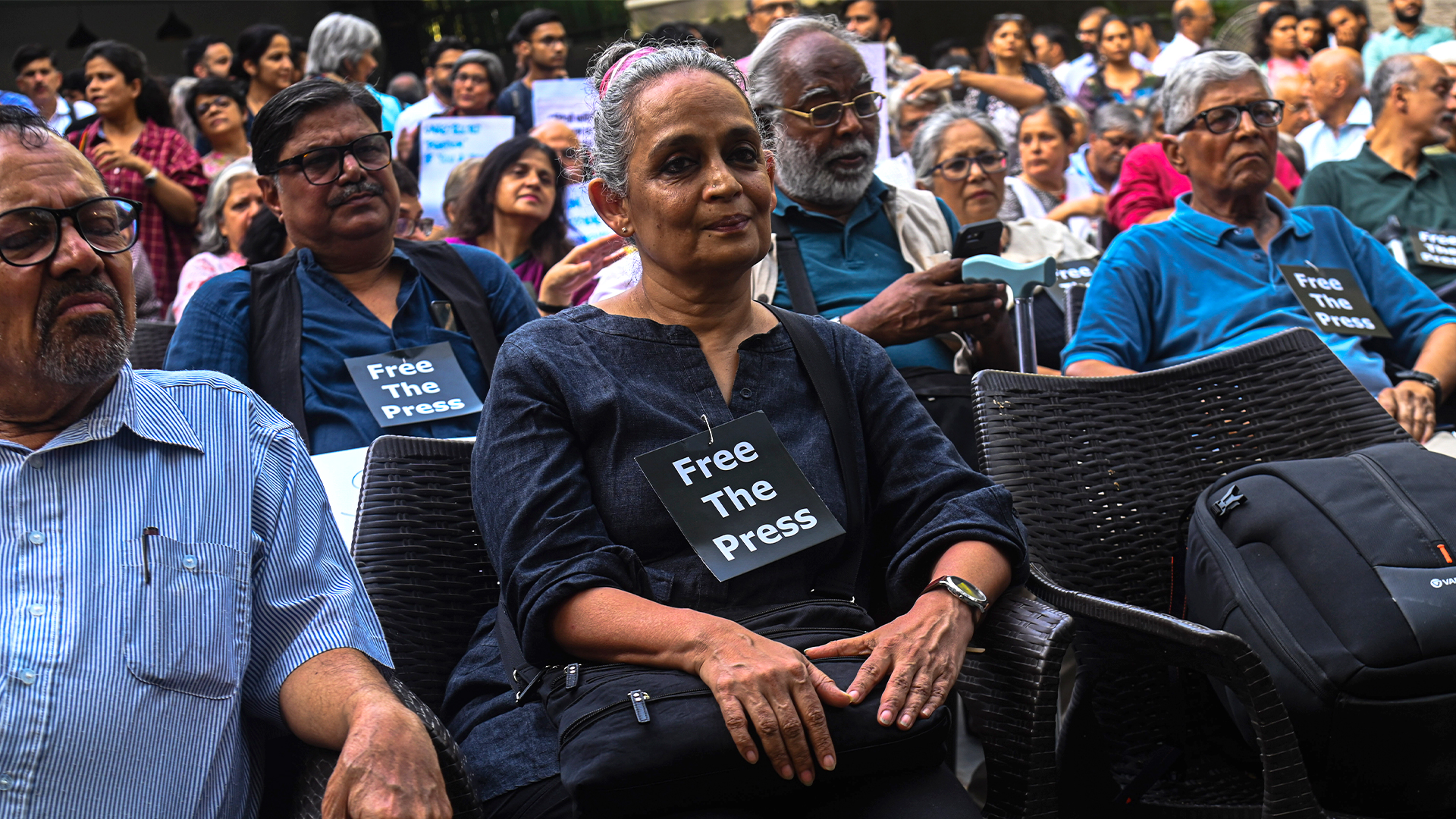
Kabir Jhangiani/NurPhoto via Getty Images
Indian journalists are being treated like terrorists for doing their jobs
When India hosted the G20 summit last month, it presented itself as the “mother of democracy” to the parade of leaders and delegations from the world’s largest economies. But at home, when the world is not watching as closely, Prime Minister Narendra Modi is systematically clamping down on free speech.
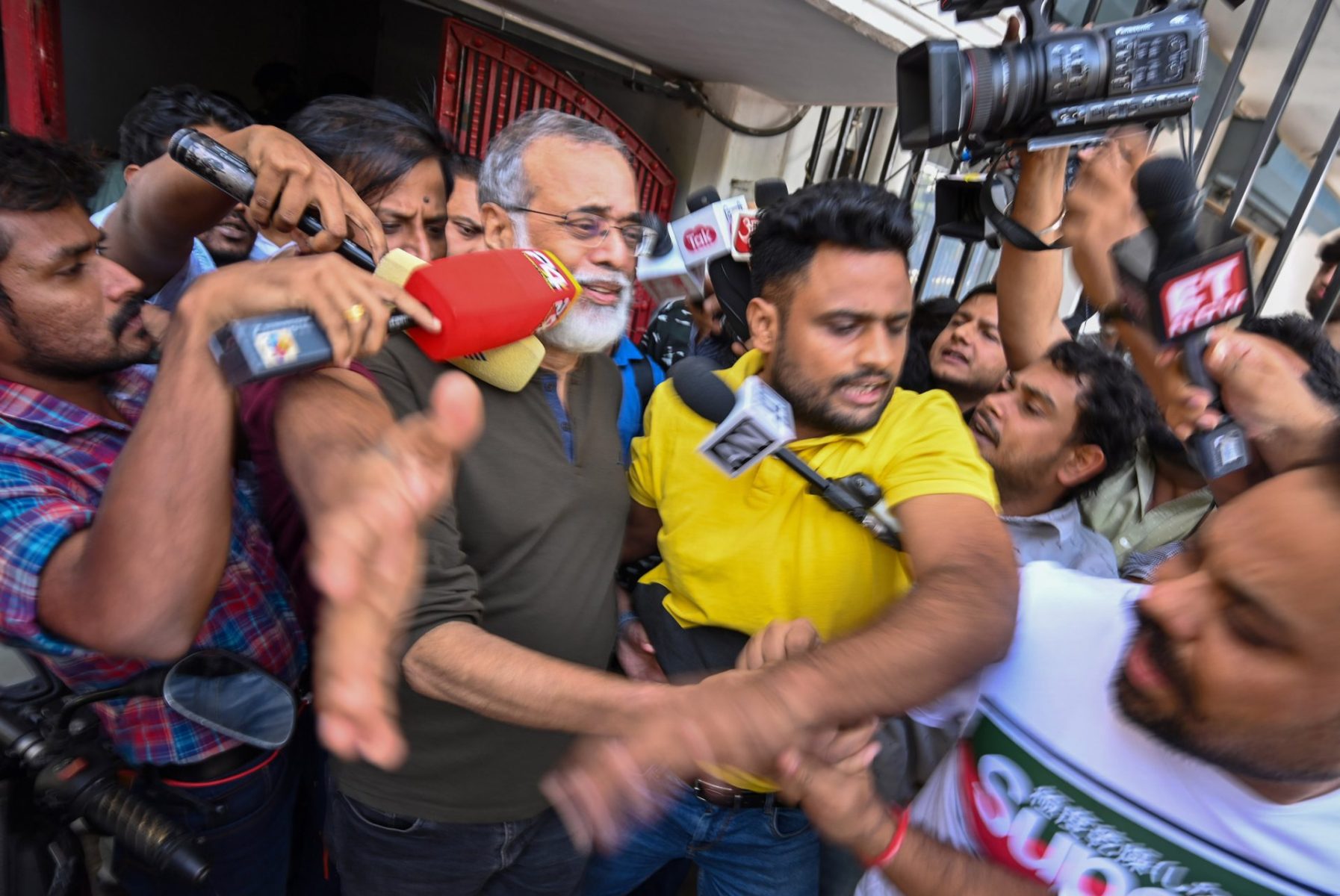
In a dramatic operation that began as the sun rose on Delhi on October 3, police raided the homes of journalists across the city. Police seized laptops and mobile phones, and interrogated reporters about stories they had written and any money they might have received from foreign bank accounts. The journalists targeted by the police work for NewsClick, a small but influential website founded in 2009 by Prabir Purkayastha, an engineer by training who is also a prominent advocate for left-wing causes and ideas.
At the time of publication, Purkayastha and a senior NewsClick executive had been held in judicial custody for 10 days. The allegations they face are classified under India’s 2019 Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, legislation that gives the government sweeping powers to combat terrorist activity.
Purkayastha, a journalist of considerable standing, is effectively being likened to a terrorist.

The day after the raids on the more than 40 NewsClick employees and contributors, a meeting was called at the Press Club of India. Among the many writers and journalists in attendance was the internationally celebrated, Booker Prize-winning author Arundhati Roy. A longtime critic of Indian government policies, regardless of the political party in power, Roy told me that India was in “an especially dangerous moment.”
She argued that the Modi government was deliberately conflating terrorism and journalism, that they were cracking down on what they described as “intellectual terrorism and narrative terrorism.” It has to do, she told me, “with changing the very nature of the Indian constitution and the very understanding of checks and balances.” She said the targeting of NewsClick, which has about four million YouTube subscribers, was intended as a warning against digital publications.
The Indian government had targeted NewsClick before, investigating what it said were illegal sources of foreign funding from China. For these latest raids, the catalyst appears to have been, at least in part, an investigation published in The New York Times in August that connected NewsClick to Neville Roy Singham, an Indian-American tech billionaire who, the story alleges, has funded the spread of Chinese propaganda through a “tangle of nonprofit groups and shell companies.”
In the lengthy article, The New York Times reporters made only brief mention of NewsClick, claiming that the site “sprinkled its coverage with Chinese government talking points.” They also quoted a phrase from a video that NewsClick published in 2019 about the 70th anniversary of the 1949 revolution which ended with the establishment of the People’s Republic of China: “China’s history continues to inspire the working classes.” But it appeared to be enough for the Delhi police to seize equipment from and intimidate even junior staff members, cartoonists and freelance contributors to the site.
Angered by the unintended consequences of The New York Times report, a knot of protestors gathered outside its New York offices near Times Square a couple of days after the raids. Kavita Krishnan, an author and self-described Marxist feminist, wrote on the Indian news and commentary website Scroll that she had warned The New York Times reporters who had contacted her for comment on the Singham investigation that their glancing reference to NewsClick would give the Modi government ammunition to harass Indian journalists.
The “NYT needs to hold its own practices up to scrutiny and ask itself if, in this case, they have allowed themselves to become a tool for authoritarian propaganda and criminalization of journalism in India,” she wrote.
While The New York Times stood by its story, a Times spokesperson told Scroll that they “would find it deeply troubling and unacceptable if any government were to use our reporting as an excuse to silence journalists.”
On October 10, a Delhi court ordered that Purkayastha and NewsClick’s human resources head Amit Chakraborty be held in judicial custody for 10 days, even as their lawyers insisted that there was no evidence that NewsClick had “received any funding or instructions from China or Chinese entities.”
India’s difficult relationship with China is at a particularly low ebb, with tens of thousands of troops amassed along their disputed borders and diplomats and journalists on both sides frequently expelled. From a Western point of view, India is also being positioned as a strategically vital counterweight to Chinese dominance of the Indo-Pacific region. Though diplomatic tensions are high, India’s trade with China has — until a 0.9% drop in the first half of this year — flourished, reaching a record $136 billion last year.
While the Indian government continues to court Chinese investment, it is suspicious of the Chinese smartphone industry — which controls about 70% of India’s smartphone market — and of any foreign stake in Indian media groups. The mainstream Indian media is increasingly controlled by corporate titans close to Modi. For instance, Mukesh Ambani and Gautam Adani, who control vast conglomerates that touch on everything from cooking oil and fashion to petroleum oil and infrastructure and who have at various points in the last year been two of the 10 richest men in the world, also own major news networks.
By March this year, Adani completed his hostile takeover of NDTV, widely considered to have been India’s last major mainstream news network to consistently hold the Modi government to account. Independent journalists and organizations such as NewsClick that report critically on the government are now out of necessity building their own audiences on platforms such as YouTube. Cutting off these organizations’ access to funds, particularly from foreign sources, helps tighten the Modi government’s grip on India’s extensive if poorly funded media.
Siddharth Varadarajan, a founder of the Indian news website The Wire, said that the actions taken against NewsClick are “an attack on an independent media organization at a time when many media organizations are singing the tune of the government.” It was not a surprise, he told me, that Delhi police were asking NewsClick journalists about their reporting on the farmers’ protests in India between August 2020 and December 2021. “While the government says it is investigating a crime on the level of terrorism, the main goal is to delegitimize and criminalize certain topics and lines of inquiry.”
The allegations against NewsClick’s Purkayastha and Chakraborty are classified under India’s Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, controversial legislation intended to give the government sweeping powers to combat terrorist activity. Under the provisions of the act, passed in 2019, the government has the power to designate individuals as terrorists before they are convicted by a court of law. It is a piece of legislation that, as United Nations special rapporteurs noted in a letter to the Indian government, undermines India’s signed commitments to uphold international human rights.
Legislative changes introduced by the Modi government include a new data protection law and a proposed Digital India Act, both of which give it untrammeled access to communications and private data. These laws also formalize its authority to demand information from multinational tech companies — India already leads the world in seeking to block verified journalists from posting content on X, the platform formerly known as Twitter — and even shut down the internet, something that it has done for days and even months on end in states across the country during periods of unrest.
India’s willingness to clamp down on freedom of information is reflected in its steep slide down the annual World Press Freedom Index. Currently ranked 161 out of 180 countries, India has slipped by 20 places since 2014 when Modi became prime minister. “The violence against journalists, the politically partisan media and the concentration of media ownership all demonstrate that press freedom is in crisis in ‘the world’s largest democracy,’” observes Reporters Without Borders, which compiles the ranking.
Atul Chaurasia, the managing editor at the Indian digital news platform Newslaundry, told me that “all independent and critical journalists feel genuine fear that tomorrow the government may go after them.” In the wake of the NewsClick raids, Chaurasia described the Indian government as the “father of hypocrisy,” an acerbic reference to the Modi government’s boasts about India’s democratic credentials when world leaders, including U.S. President Joe Biden, arrived in Delhi in September for the G20 summit.
When Biden and Modi held a bilateral meeting in Delhi before the summit began, Reuters reported that “the U.S. press corps was sequestered in a van, out of eyesight of the two leaders — an unusual situation for the reporters and photographers who follow the U.S. President at home and around the world to witness and record his public appearances.” Modi himself, despite being the elected leader of a democracy for nearly 10 years, has never answered questions in a press conference in India.
Instead, Modi addresses the nation once a month on a radio broadcast titled “Mann ki baat,” meaning “words from the heart.” And he very occasionally gives seemingly scripted interviews to friendly journalists and fawning movie stars.
As for unfriendly journalists, Purkayastha is currently in judicial custody while a variety of Indian investigative agencies are on what Arundhati Roy called a “fishing expedition,” rooting through journalists’ phones and NewsClick’s finances and tax filings in search of evidence of wrongdoing. Varadarajan of the Wire told me that the message being sent to readers and viewers of NewsClick and other sites intent on holding the Modi government to account was clear: “Don’t trust their content and don’t even think about giving them money because they are raising money for anti-national activities.”

Since my conversation with Roy at the Press Club of India on October 4, it has been reported that she faces the possibility of arrest.
Delhi’s lieutenant governor — an official appointed by the government and considered the constitutional, if unelected, head of the Indian capital — cleared the way for her to be prosecuted for stating in 2010 that in her opinion, Kashmir, the site of long-running territorial conflict between India and Pakistan, has “never been an integral part of India.” A police complaint was filed 13 years ago, but Indian regulations require state authorities to sign off on prosecutions involving crimes such as hate speech and sedition. Now they have.
Apar Gupta, a lawyer, writer and advocate for digital rights, describes the Modi government’s eagerness to use the law and law enforcement agencies against its critics as “creating a climate of threat and fear.” Young people especially, he told me, have to have “extremely high levels of motivation to follow their principles because practicing journalism now comes with the acute threat of prosecution, of censorship, of trolling, and of adverse reputational and social impacts.”
A young NewsClick reporter, requesting anonymity, told me that “with every knock at the door, I feel like they’ve finally come for me.” They described the paranoia that had gripped their parents: “My father now only contacts me on Signal because it’s end-to-end encrypted. I could never have imagined any of this.”
Following the NewsClick raids, Rajiv Malhotra, an Indian-American Hindu supremacist ideologue, appeared on a major Indian news network to openly call for the Modi government to target even more independent journalists. Malhotra singled out the People’s Archive of Rural India (PARI), a website founded by P. Sainath, an award-winning journalist committed to foregrounding the perspectives of rural and marginalized people.
On what grounds does Malhotra suggest that the Modi government go after Sainath and PARI? The site, Malhotra told the newscaster, who does not interrupt him, encourages young villagers, Dalits (a caste once referred to as “untouchable”), Muslims and other minorities to “tell their story of dissent and grievances against the nation state.”
Criticism of the nation and its authorities, in other words, is akin to sowing division. Whether it’s an opinion given in 2010 or a reference to Chinese funding within an article from a newspaper loathed by supporters of Modi and his Hindu nationalist ideology, the Indian government will apparently use any excuse to silence its critics.
The story you just read is a small piece of a complex and an ever-changing storyline that Coda covers relentlessly and with singular focus. But we can’t do it without your help. Show your support for journalism that stays on the story by becoming a member today. Coda Story is a 501(c)3 U.S. non-profit. Your contribution to Coda Story is tax deductible.