AFP via Getty Images
Sectarian violence in Manipur is a mirror for Modi’s India
Speaking in Hindi, from the ramparts of Delhi’s monumental, 17th-century Red Fort, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi ran through a laundry list of his government’s achievements over the last nine years. August 15 marked his 10th consecutive Independence Day address. If he gives an 11th, it will be as prime minister for a third five-year term. India goes to the polls next year, and Modi is widely anticipated to secure a return to power.
In the course of a 90-minute address, laden with emotion, exhortation and self-congratulation, Modi dwelled in passing on the continuing violence in Manipur, a state in the northeast of India. The “nation stands with the people of Manipur,” he said. A resolution to the problems, he added, could only be achieved through peace, a goal toward which the federal and state governments were working.
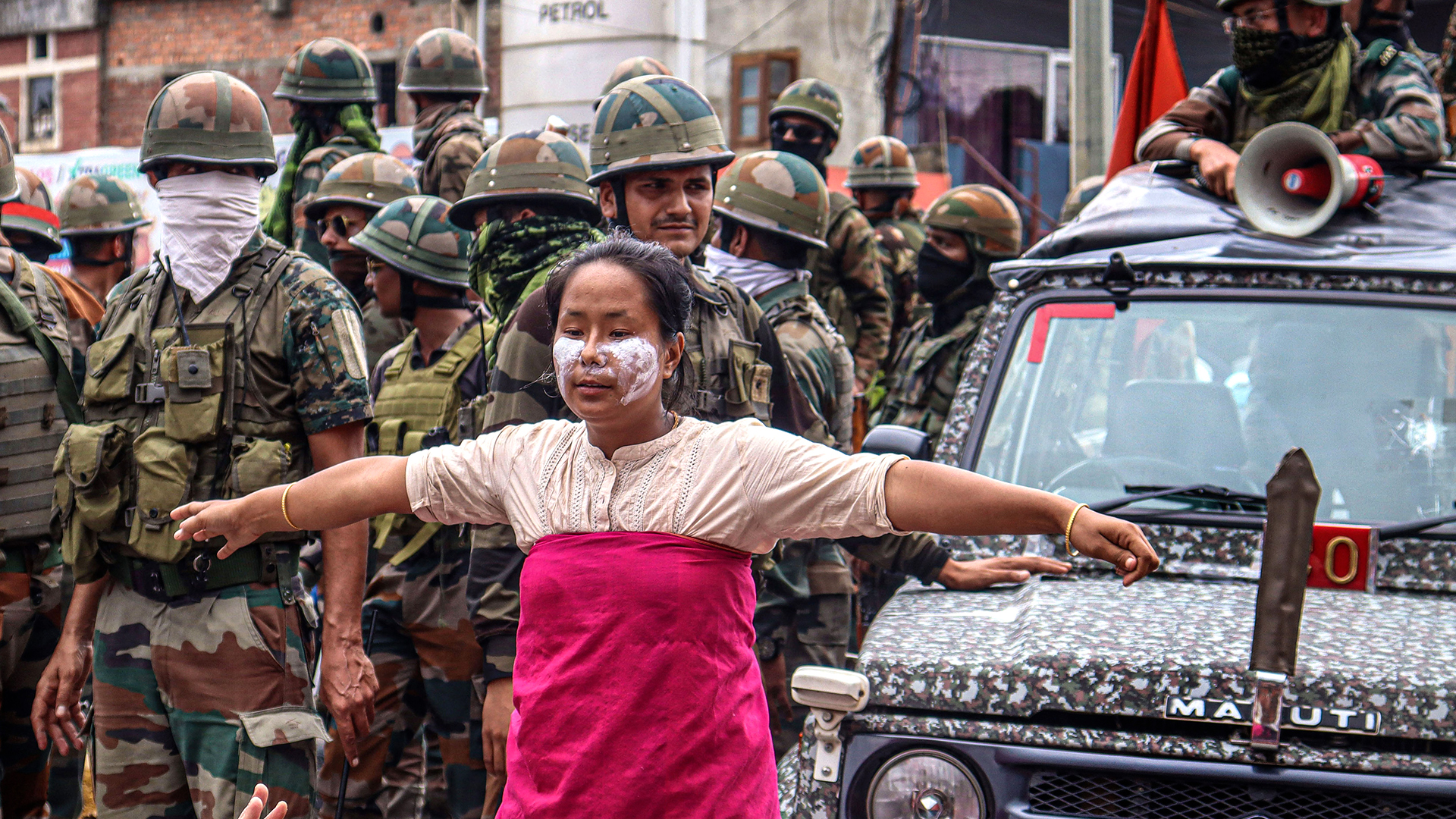
If the sentiments seem boilerplate compared to Modi’s usual mode of rhetorical excess, it is because the Indian prime minister has gone to extraordinary lengths to avoid talking about Manipur. The small state, bordering Myanmar, has been in tumult since May, with at least 200 people killed during riots, over 60,000 displaced and with houses, churches and whole villages set ablaze.
As the leaders of the world’s largest economies arrive in India on September 9 for the two-day G20 summit, the culmination of India’s presidency of the intergovernmental group, Modi is expecting to put on a show. Delhi, or at least its most prominent areas, is being given a hasty and glitzy makeover. But the gleam might be tarnished by deepening sectarian rifts Modi’s government cannot appear to get under control and might indeed have helped unleash.
Even the Indian army, sent in to quell the violence in Manipur, has struggled to cope. The fighting has taken place between the largely Hindu Meitei people of the valley and the largely Christian Kuki tribes from the hills. It began over a high court order that granted Meitei people certain affirmative action rights, despite their existing political and financial muscle in Manipur. The complexity of the conflict is exacerbated by certain land laws intended to protect tribal lands in the hills,which the Meiteis say unfairly confine them to the valley.
It is true that animosity between the Kuki tribes and the Meiteis in Manipur dates back over a decade, but the inability of the authorities to calm the current violence is due to the perceived biases of the Meitei-led state government of Manipur. Its chief minister, Biren Singh, a Meitei, has as recently as July 1 — nearly two months after the violence began splitting his state apart — been taunting Kukis on social media. “Are you from India or Myanmar,” he responded to a critic on X, the company formerly known as Twitter, before deleting his post.
Meiteis allege that an influx of illegal immigrants from Myanmar, mostly ethnic Kukis, are upsetting the demographic balance of Manipur and claim that the newcomers are cultivating poppy fields in the hills as part of a rampant drug trade.
During India’s recent parliamentary session, between July 20 and August 11, the opposition brought a motion of no confidence against the Modi government. It was, as expected, easily defeated. Modi’s party, the Bharatiya Janata Party, holds a large majority and faced down a no-confidence motion in 2021 with similar ease.
Still, the motion provided an opportunity for the opposition to criticize the government’s lack of response to violence in Manipur and to force both the prime minister and the home minister, Amit Shah, to address the issue. Shah, who continues to back Manipur’s chief minister Singh, parroted the line that Kukis, whose ranks were allegedly being bolstered by illegal immigrants from Myanmar, were largely responsible for the clashes.
A mainstream Kuki group described Shah’s explanation as “extremely unfortunate as it is largely speculative with no valid proof or evidence.” It went on to say that Shah, by making his “abhorrent, nonsensical and disastrous” remarks, had chosen to “sacrifice the Kukis at the altar of Biren Singh.”
Meanwhile, on August 10, Modi responded in parliament to the no-confidence motion. He spoke for over two hours. It took more than 90 minutes for him to even broach the topic of Manipur, by which time the opposition had walked out in protest.
Modi blamed the Congress party, the main opposition faction, for having mismanaged the northeastern region of India since the country’s independence from the British Empire was won in 1947. The Congress has governed for about 50 of India’s 76 years as an independent country and has been caricatured by Modi as a party grown rotten on power and assumed privilege.
Despite being prime minister for nearly a decade, Modi scarcely speaks without blaming the Congress and India’s first prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru, in particular, for holding India back from its rightful status as a global superpower. In May, while Manipur quite literally burned, Modi was on a triumphant global tour, including trips to Australia and the United States where much was made of India’s emerging power status.
“Blaming the Congress for everything that is happening in Manipur,” said Kham Khan Suan Hausing, a political science professor at Hyderabad University, “is a bit far-fetched.” The “culpability and complicity of the BJP government,” he told us, “has to be called out.” Last week, Hausing was granted protection from arrest by India’s Supreme Court on charges that he had defamed the Meitei community in an interview with the Indian news website The Wire.
According to Hausing, Shah has revealed his “gross incompetence and apparent lack of intelligence on the ground” by blaming the Kukis alone for the riots in Manipur. And Modi, he told us, “appears more interested in media management than in the structural causes of the violence.” These forthright views have made Hausing a target of what he calls a “smear campaign by vigilante trolls,” who have questioned his legal status as an Indian. It is a typical line of attack used against Kukis like him, Hausing says, who are derided as immigrants from Myanmar. “The smears smack of how ignorant and ill-informed public discourse is about citizenship.”
Writing in the New York Times this month, the author Debasish Roy Chowdhury argues that “it’s a signature tactic of modern day despots: tightening their grip on power by redefining who belongs to the polity and ostracizing others.” Any perceived slight against Modi is treated by his supporters, and often by Modi himself, as a slight against India.
During his long speech decrying the no-confidence motion last week, Modi said, in Hindi, that the motion had little to do with violence in Manipur but was instead an attempt to “defame India.” They “have no faith in the people of India,” Modi said of the opposition, “in the abilities of India. They have tried in vain to break the self-confidence of Indians with this no-confidence vote.”
In his Independence Day address on August 15, Modi took a similarly proprietorial tone, referring to Indian voters as his family and offering personal guarantees of Indian success. It was, said the longtime Congress politician and leader Jairam Ramesh, a “crass election speech filled with distortions, lies, exaggerations and vague promises.” He added that Modi had made an annual address to the nation by its prime minister “all about himself and his image.”
Sharad Pawar, another longtime politician and major opposition figure, told the audience at a public rally on August 14 that the “Modi government has been a mute spectator to what has been happening in Manipur.” Modi was initially jolted out of that studied silence by a video that made global headlines last month of two Kuki women in Manipur being paraded naked and sexually assaulted by a Meitei mob. Even then, he did not address the conflict directly, only condemning the assault as “shameful.”
The BJP then asked X to take the video down because it was fomenting further violence. In fact, the BJP-led government in Manipur has imposed a shutdown of mobile internet services in the state, which has been in effect since May 3. At the time of writing, services have still not been fully restored, causing untold economic damage with little evidence that the shutdown has served its purpose of lessening violence due to misinformation and rumor-mongering.
If it seems surprising that the leader of a democracy can get away with saying so little about a sectarian war breaking out in a state, it is in keeping with Modi’s tried and tested strategy. Sectarian identity is increasingly contested in the BJP’s majoritarian, Hindu nationalist conception of India. While Modi talks about democracy and pluralism as formative parts of India’s identity on foreign visits, at home, nerves are fraying.
On July 31, even as the opposition was insisting that the prime minister address violence in Manipur before the parliament, sectarian riots were breaking out in the state of Haryana, which borders the Indian capital Delhi. A procession organized by a notorious Hindu nationalist organization devolved into street fights as it passed through the district of Nuh. Just as outsiders, particularly illegal Kuki immigrants from Myanmar, were blamed by the BJP for fanning the flames in Manipur, Muslim Rohingya refugees from Myanmar were promptly blamed for the violence in Haryana.
Modi is fond of referring to “double engine” governments — his dream of BJP governments at both federal and state levels, working together to foster more development. Both Manipur and Haryana are run by BJP governments at the state level. The double engine seems to work, then, to reinforce the BJP’s political majoritarianism, its instinctive support for Hindus in any sectarian conflict.
Peace and resolution in Manipur can only return, says Gaurav Gogoi, a Congress member of parliament, “when you can win people’s trust.” And that trust, he told us, speaking in Hindi, “can only be won when the BJP takes responsibility.” According to Gogoi, Manipur is still a tinderbox, despite Modi’s claims that peace is returning. He alleges that “6,000 weapons have been looted from police stations and not ordinary weapons but AK47s and bombs.” Gogoi, who led the no-confidence motion in parliament, told us that it is the BJP’s politics at both state and federal levels that has “split Manipur into two.” It is a pattern of division, he notes, that is evident in communal violence across India, including most recently in Haryana.
In his August 15 address to the nation, Modi said his time as prime minister had led to a “new trust, a new hope and a new attraction” toward India around the world. But if Modi is stoking hope abroad, there is evidence enough to say that he is stoking division at home.
The story you just read is a small piece of a complex and an ever-changing storyline that Coda covers relentlessly and with singular focus. But we can’t do it without your help. Show your support for journalism that stays on the story by becoming a member today. Coda Story is a 501(c)3 U.S. non-profit. Your contribution to Coda Story is tax deductible.