Vinay Santosh Kumar/Hindustan Times via Getty Images
The movement to expel Muslims and create a Hindu holy land
- Photography by Alishan Jafri
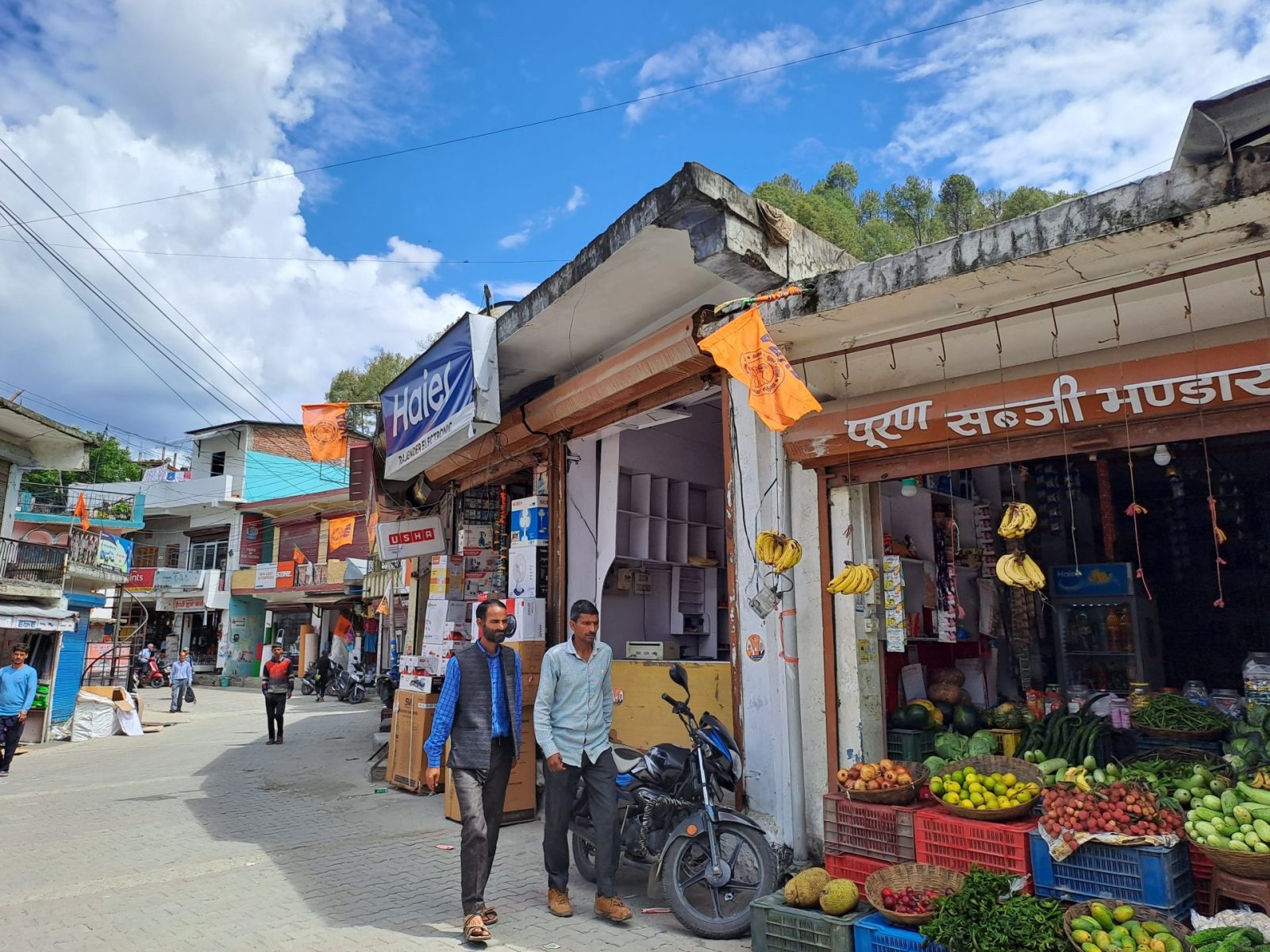
Late on a hot night this summer, Mohammad Ashraf paced around his house, wondering if the time had finally come for him to flee his home of 40 years. Outside his window lay the verdant slopes of the Himalayas. All of Purola, a small mountain village in the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand, appeared to be asleep, tranquil under the cover of darkness. But Ashraf was awake. Could he hear noises? Were those footsteps beneath his window? Did his neighbors mean to do him harm?
“I was very afraid,” Ashraf said. “My kids were crying.”
Since May 29, there had been unrest in Purola. The local chapter of India’s governing Bharatiya Janata Party, along with several other right wing Hindu nationalist groups, had staged a rally in which they demanded that local Muslims leave town before a major Hindu council meeting scheduled for June 15. On June 5, Ashraf’s clothing shop, like the shops of other Muslim traders, was covered with posters that warned “all Love Jihadis” should leave Purola or face dire consequences. They were signed by a Hindu supremacist group called the “Dev Bhoomi Raksha Abhiyan,” or the Movement to Protect God’s Land.
The rally in Purola was the culmination of anti-Muslim anger and agitation that had been building for a month. Earlier in May, two men, one Muslim and one Hindu, were reportedly seen leaving town with a teenage Hindu girl. Local Hindu leaders aided by the local media described it as a case of “love jihad,” a reference to the conspiracy theory popular among India’s Hindu nationalist right wing that Muslim men are seeking to marry and convert Hindu women to Islam. Public outrage began to boil over. The men were soon arrested for “kidnapping” the girl, but her uncle later stated that she had gone willingly with the men and that the charges were a fabrication.
It mattered little. Hindu organizations rallied to protest what they claimed was a spreading of love jihad in the region, whipping up the frenzy that had kept Ashraf’s family up at night, fearing for their safety.

What is happening in Uttarakhand offers a glimpse into the consequences of the systematic hate campaigns directed at Muslims in the nine years since Narendra Modi became prime minister. Hindu nationalists believe that the Hindu-first ideology of the government means they have the support necessary to make the dream of transforming India into a Hindu rather than secular nation a reality. Muslims make up about 14% of the Indian population, with another 5% of the Indian population represented by other religious minorities including Christians. In a majoritarian Hindu India, all of these minorities, well over 250 million people, would live as second-class citizens. But it is Muslims who have the most to fear.
Not long after the events in Purola, Modi would go on a highly publicized state visit to the United States. “Two great nations, two great friends and two great powers,” toasted President Joe Biden at the state dinner. The only discordant note was struck at a press conference — a rarity for Modi who has never answered a direct question at a press conference in India since he became prime minister in 2014. But in Washington, standing alongside Biden, Modi agreed to answer one question from a U.S. journalist. The Wall Street Journal’s Sabrina Siddiqui was picked. “What steps are you and your government willing to take,” she asked Modi, “to improve the rights of Muslims and other minorities in your country and to uphold free speech?”
In his answer, Modi insisted that democracy was in the DNA of India, just as it was in the U.S. For daring to ask the question, Siddiqui was trolled for days, the victim of the sort of internet pile-on that has become a familiar tactic of the governing BJP and its Hindu nationalist supporters. In the end, a White House spokesperson, John Kirby, denounced the harassment as “antithetical to the principles of democracy.”
Modi has received warm, enthusiastic welcomes everywhere from Sydney and Paris to Washington. In every country he visits, Modi talks up India as a beacon of democracy, plurality and religious tolerance. But as India prepares for elections in 2024, and Modi expects to return to office for a third consecutive five-year term, the country is teetering between its constitutional commitment to secular democracy and the BJP’s ideological commitment to its vision of India as a Hindu nation.
In a sharply worded critique of Modi’s state visit to the U.S., author Arundhati Roy, writing in The New York Times, noted that the State Department and the White House “would have known plenty about the man for whom they were rolling out the red carpet.” They might, she wrote, “also have known that at the same time they were feting Mr. Modi, Muslims were fleeing a small town in northern India.”

Roy was referring to the right wing Hindu rallies in Uttarakhand. On May 29, a thousand people marched across Purola, chanting “Jai Shri Ram” — a phrase once used as a greeting between observant Hindus that has in the recent past become a battle cry for Hindu nationalists. During the rally, the storefronts of Muslim-run shops were defaced and property was damaged. The police, walking alongside the mob, did nothing to stop the destruction. Several local BJP leaders and office-bearers participated in the march. A police official later told us that the rally had been permitted by the local administration and the town’s markets were officially shut down to allow for the demonstrations.
As the marchers advanced through the town’s narrow lanes, Ashraf said they intentionally passed by his home. His family, one of the oldest and most well-established Muslim families in Purola, has run a clothing shop in Purola for generations. Ashraf was born in the town and his father moved to Purola more than 40 years ago.
“They came to my gate and hurled abuse,” he said. “Drive away the love jihadis,” the crowd screamed. “Drive away the Muslims.”
Among the slogans was a particularly chilling one: “Muslim mukt Uttarakhand chahiye.” They wanted an Uttarakhand free of Muslims, they said in Hindi. A call, effectively, for ethnic cleansing.
Ashraf’s three young children watched the demonstration from their window. “My 9-year-old,” he told us, “asked, ‘Papa, have you done something wrong?’”
Forty Muslim families fled Purola, a little under 10% of its population of 2,500 people. Ashraf’s was one of two families who decided to stay. “Why should I leave?” he asked. “Everything I have is here. This is my home. Where will I go?”

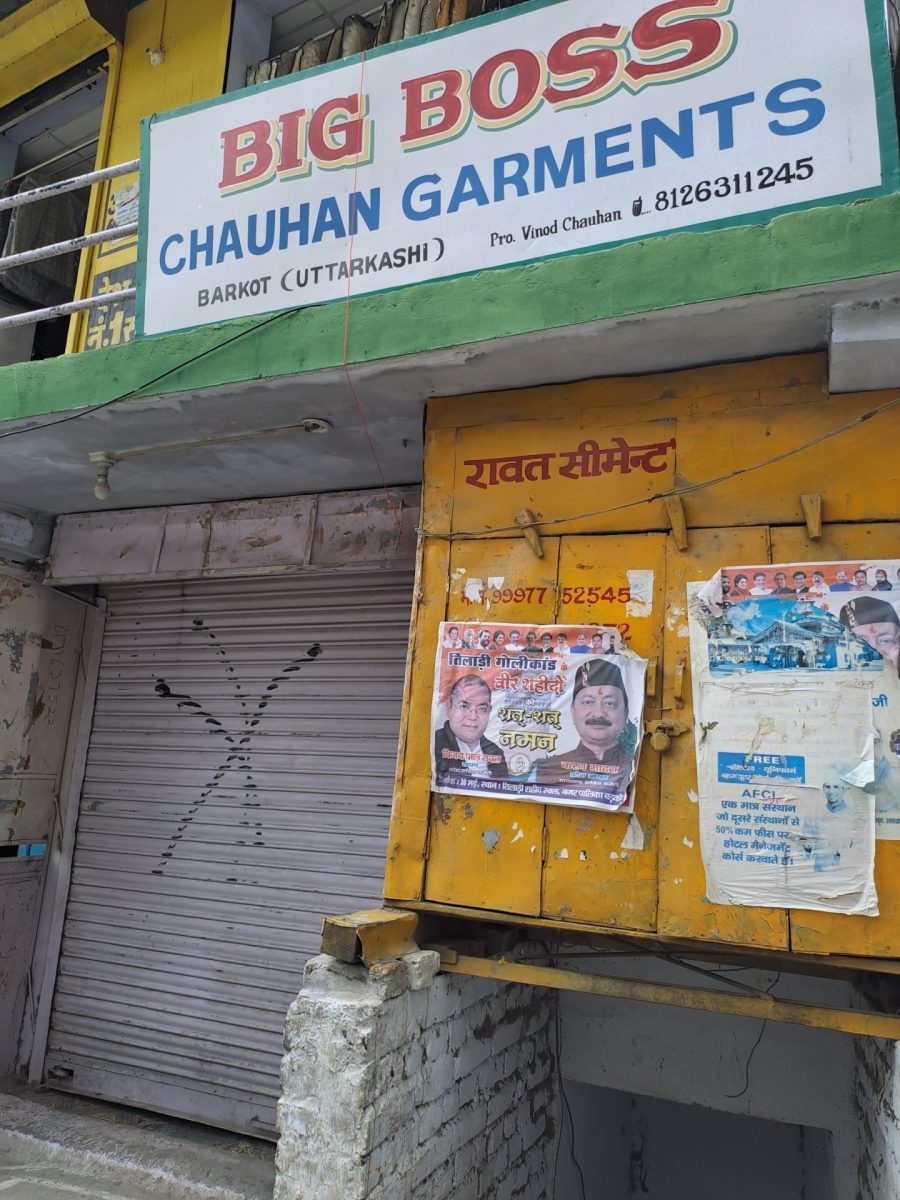
The campaign in Purola spread quickly to other parts of the state. On June 3, a large rally took place in Barkot, another small mountain town in Uttarakhand, about an hour’s drive from Purola. Thousands marched through the town’s streets and neighborhoods as a loudspeaker played Hindu nationalist songs. “Har Ghar Bhagwa Chhayega, Ram Rajya Ab Aayega” — Every House Will Fly the Hindu Flag, Lord Ram’s Kingdom Is Coming.
Muslim shopkeepers in the town’s market, like the Hindu shopkeepers, had pulled their shutters down for the day, anticipating trouble at the rally. As the mob passed by the shops, they marked each Muslim-run shop with a large black X. The town’s Muslim residents estimate that at least 43 shops were singled out with black crosses. Videos taken at the rally, shared with us, showed the mob attacking the marked-up Muslim shops to loud cheers from the crowd. The police stood by and watched.
One Muslim shopkeeper, speaking anonymously for fear of retribution, described arriving at his shop the next day and seeing the large black cross. “My first thought was ‘Heil Hitler,’” he said. “I have read Hitler’s history. That’s how he had marked out Jews. It is the same strategy. That’s how we are being identified.”
We spoke to dozens of people who identify with and are members of Hindu nationalist parties, ranging from Modi’s BJP to fringe, far-right militant groups such as the Bajrang Dal, analogous in some ways to the Proud Boys. Again and again, we were told that just as “Muslims have Mecca and Christians have the Vatican,” Hindus need their own holy land. Uttarakhand, home to a number of important sites of pilgrimage, is, in this narrative, the natural home for such a project —if only, the state could rid itself of Muslims, or at the very least monitor and restrict their movement and forbid future settlement. Nearly 1.5 million Muslims currently live in Uttarakhand, about 14% of the state’s entire population, which exactly reflects the proportion nationally.
Hindu nationalists told us how they are working to create and propagate this purely Hindu holy land. Their tactics include public rallies with open hate speech, village-level meetings and door-to-door campaigns. WhatsApp, Facebook and YouTube are essential parts of their modus operandi. These were tools, they said, to “awaken” and “unite” Hindus.
Their attempts to portray Muslims as outsiders in Uttarakhand dovetails with a larger national narrative that Hindus alone are the original and rightful inhabitants of India. The BJP’s ideological parent, the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh, founded in 1925, argues that India is indisputably a “Hindu rashtra,” a Hindu nation, nevermind what the Indian constitution might say.



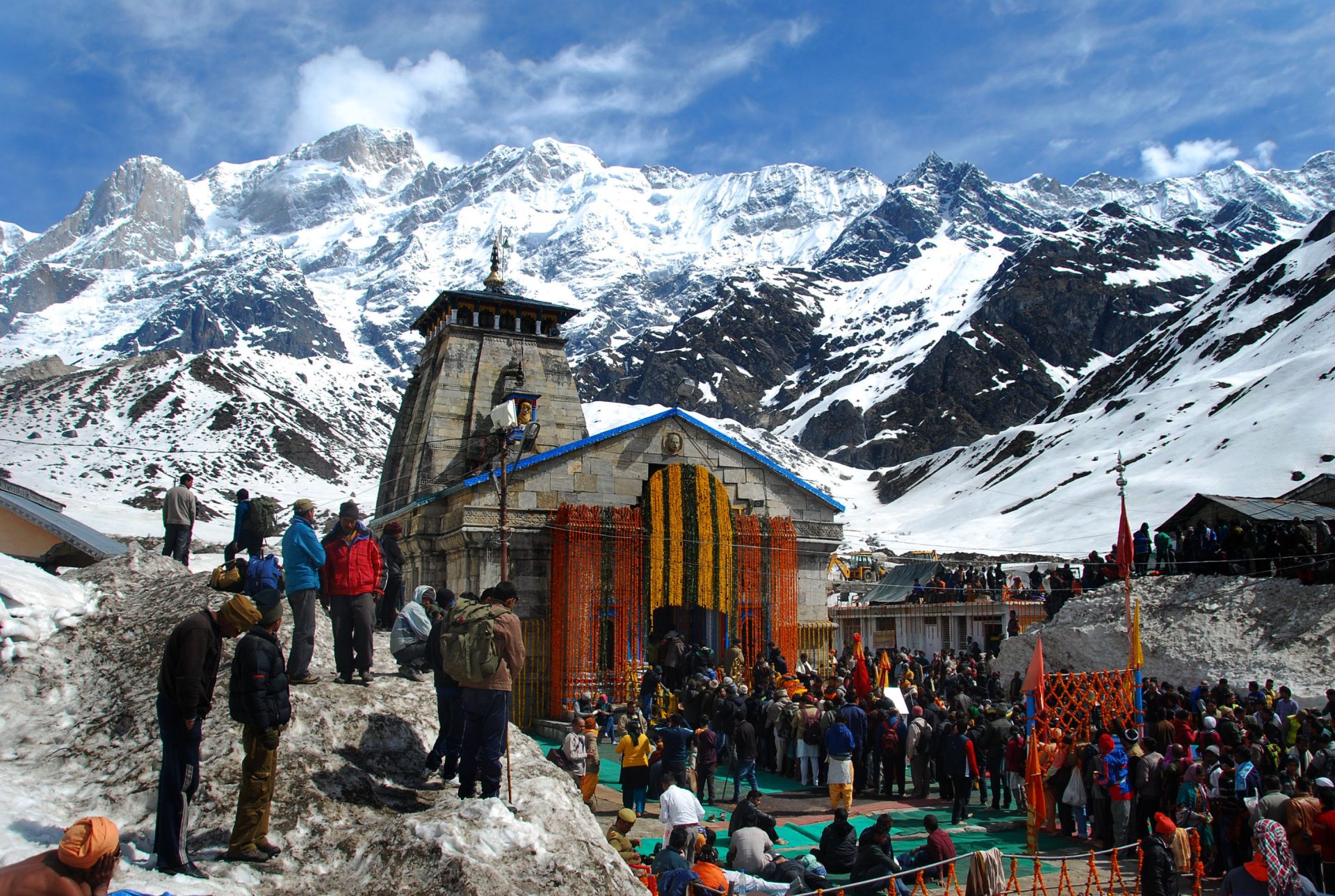
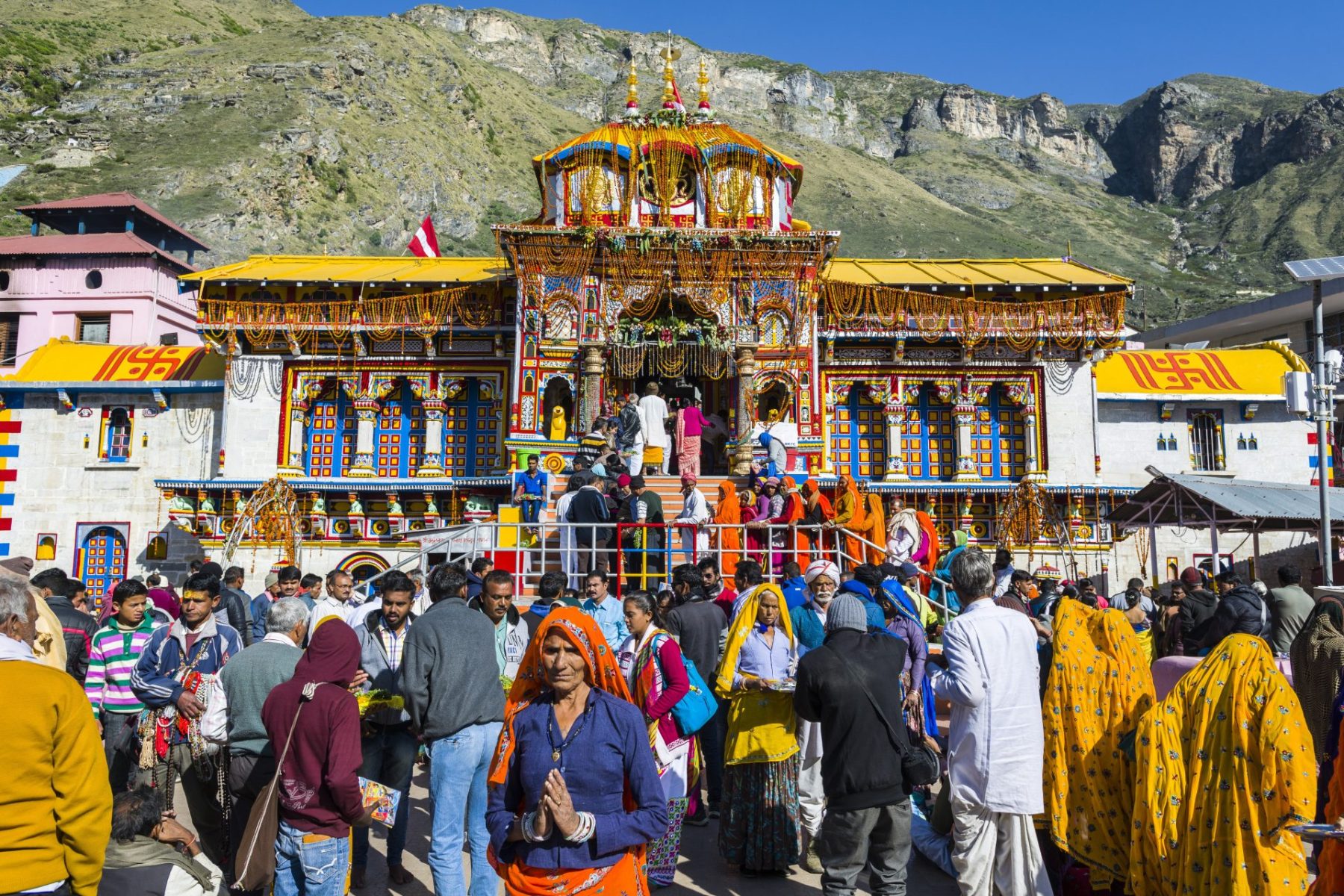
With a population of 11.5 million, Uttarakhand stretches across the green Himalayan foothills. It is a prime tourist destination known for its imposing mountains, cascading white rivers and stone-lined creeks. It is home to four key Hindu pilgrimage sites — the sources of two holy rivers, the Ganges and the Yamuna; and Kedarnath and Badrinath, two temples dedicated to the Hindu gods Shiva and Vishnu respectively. Together, these four sites, high up in rugged mountain terrain, form a religious travel circuit known as the Chota Char Dham. According to state government figures, over 4 million pilgrims visited these sites in 2022 alone. Downhill, Haridwar, a town on the banks of the Ganges, is of such spiritual significance that Hinduism’s many seers, sages and priests make it their home. For Hindus in north India, Uttarakhand is the center of 4,000 years of tradition.
The state of Uttarakhand is also one of India’s newest — formed in November 2000, carved out of Uttar Pradesh, a huge, densely populated north Indian state. Its creation was the result of a long socio-political movement demanding a separate hill state with greater autonomy and rights for its many Indigenous peoples, who form just under 3% of the state’s population and are divided into five major tribal groups. These groups are protected by the Indian constitution, and their culture and beliefs are distinct from mainstream Hindu practice. But over the last decade, Uttarakhand has seen its identity shift from a mountain state created to better represent its Indigenous population to one molded and marketed primarily as “Dev Bhoomi,” a sacred land for Hindus.
Since becoming prime minister, Modi has made at least six trips to the state’s key pilgrimage sites, each time amidst much hype and publicity. In May 2019, in the final stages of the month-long general election, Modi spent a day being photographed meditating in a remote mountain cave, less than a mile from the Kedarnath shrine. Images were beamed around the country of Modi wrapped in a saffron shawl, eyes closed, sitting cross-legged atop a single wooden bed. The symbolism was not lost on Hindus — the mountains and caves of Uttarakhand are believed to be the abode of the powerful, ascetic Shiva, who is often depicted in deep meditation on a mountain peak.
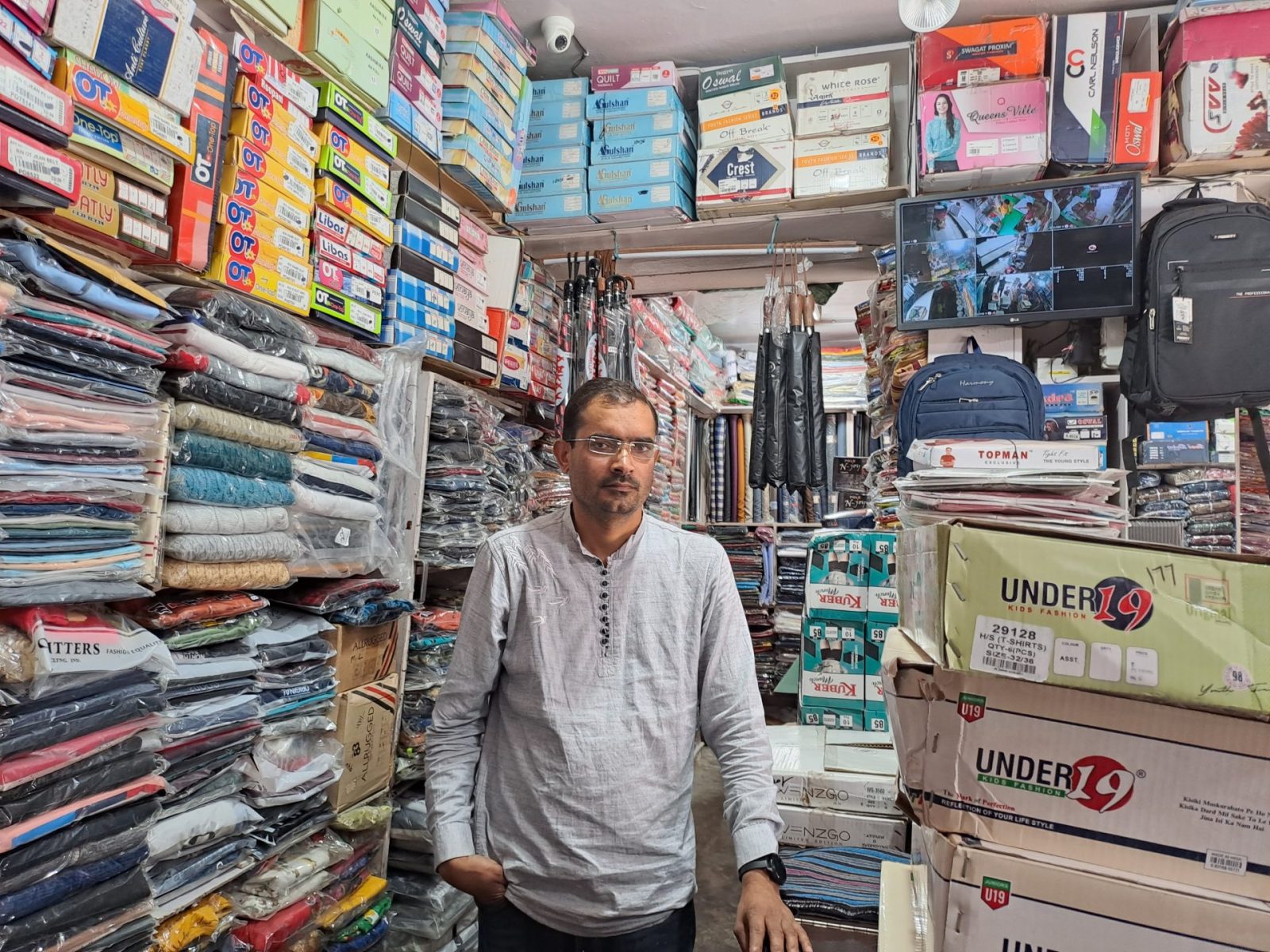
Like other Muslims in Purola, Zahid Malik, who is a BJP official, was also forced to leave his home. We met him in the plains, in the town of Vikasnagar, to where he had fled. He said Hindus had threatened to set his clothing shop on fire. “If I, the BJP’s district head, face this,” he told us, “imagine what was happening to Muslims without my connections. For Hindus, all of us are jihadis.”
Malik emphasized that Muslims have lived for generations in the region and participated in the creation of Uttarakhand. “We have been here since before the state was made,” Malik told us. “We have protested. I myself have carried flags and my people have gone on hunger strikes demanding the creation of this state, and today we are being kicked out from here like you shoo away flies from milk.”
For Malik, the irony is that it is members of his own party who want people like him out of Uttarakhand.
Ajendra Ajay is a BJP leader and the president of the Badrinath Kedarnath Temple Committee, an influential post in a state dominated by the pilgrimage economy. “In the mountain regions, locals are migrating out,” he told us, “but the population of a certain community is increasing.” He means Muslims, though he offered no numbers to back his claims. Nationally, while the Muslim birth rate is higher than that of other groups, including Hindus, it is also dropping fast. But the supposed threat of Muslims trying to effect demographic change in India through population growth is a standard Hindu nationalist trope.
“Uttarakhand is very sacred for Hindus and the purity of this land, its special religious and cultural character, should be maintained,” Ajay said. His solution to maintaining interreligious harmony is to draw stricter boundaries around “our religious sites” and to enforce “some restrictions on the entry of non-Hindus into these areas.”

On our way to Purola, the thin road snaking around sharp mountain bends, we stopped at another hill town by the Yamuna river. Naugaon is a settlement of approximately 5,000 people, many of whom are rice and potato farmers. The town’s center has a small strip of shops that sell clothes, sweets and medicines. In another era, it might have been possible to imagine a tiny, remote spot like this being disconnected from the divisive politics of the cities. But social media and smartphones mean Naugaon is no longer immune. While technology has bridged some divides, it has exacerbated others.
News of the public rallies in Purola in which Hindu supremacists demanded that Muslims either leave or be driven out spread quickly. In Naugaon, a new WhatsApp group was created. The group’s name, translated from Hindi, was “Hinduism is our identity.” By the end of June, it had 849 members. Deepak Rawat, a pharmacist in the Naugaon market, was among the participants. “People are becoming more radicalized,” he said approvingly, as he scrolled through posts on the group.
People we met in Naugaon told us there had already been a campaign in 2018 to drive Muslims away from this tiny rural outpost. “We chased them out of town,” they told us.
Sumit Rawat, a farmer in Nuagaon, described what happened. According to him, a young Hindu girl had been kidnapped by a Muslim waste-picker and was rescued by passersby who heard her cries for help. (We were not able to independently corroborate Rawat’s claims.) He told us that Hindus marched in protest at the attempted abduction. Their numbers were so great, said Rawat, that the rally stretched a mile down the market street. With little reporting of these incidents in the national press, people in cities are largely unaware of the rage that seethes in India’s rural towns and villages. “We want Muslims here to have no rights,” Rawat told us. “How can we trust any of them?”

In Dehradun, the Uttarakhand capital, we met Darshan Bharti, a self-styled Hindu “saint” and founder of the “Dev Bhoomi Raksha Abhiyan,” or the Movement to Protect God’s Land. He was dressed in saffron robes and a string of prayer beads. The room in which we sat had swords hung on the orange walls. His organization was behind the posters pasted on shops in Purola owned by Muslims, ordering them to leave town.
On June 7, with the anti-Muslim demonstrations in Purola still in the news, Bharti posted a picture on his Facebook page with Kumar, the state’s police chief. Even as Bharti spoke of inciting and committing violence, he dropped the names of several politicians and administrators in both the state and national governments with whom he claimed to be on friendly terms. In the room in which we met, there was a photograph of him with the current national security adviser, Ajit Doval, among a handful of figures believed to wield considerable influence over Modi.
Bharti also claims to have met Pushkar Singh Dhami, the Uttarakhand chief minister, the highest elected official in the state, on several occasions. He has posted at least two pictures of these meetings on his social media accounts. He described Dhami as his disciple, his man. “All our demands, like dealing with love jihad and land jihad, are being met by the Uttarakhand government,” Bharti said. Land jihad is a right wing conspiracy theory that claims Muslims are illegally encroaching on Hindu land to build Muslim places of worship.
We met Ujjwal Pandit, a former vice president of the BJP’s youth wing and now a state government functionary, at a government housing complex on the banks of the Ganges in Haridwar. It didn’t take long for him to claim that Muslims were part of a conspiracy to take over Uttarakhand through demographic force. In Uttarakhand, he said, guests were welcome but they had to know how to behave.
Pandit claimed, as have BJP leaders at state and national levels, that no Muslims had been forced to leave Purola, that those who left had fled on their own accord. As the red sun set behind us into the Ganges, he said quietly, “This is a holy land of saints. Sinners won’t survive here.”
The story you just read is a small piece of a complex and an ever-changing storyline that Coda covers relentlessly and with singular focus. But we can’t do it without your help. Show your support for journalism that stays on the story by becoming a member today. Coda Story is a 501(c)3 U.S. non-profit. Your contribution to Coda Story is tax deductible.