Teona Tsintsadze/Getty Images
Life on Earth, after humans
The Anthropocene refers to the idea that, particularly since the mid-20th century, humans have created a new geological epoch through our transformational impact on the Earth. Earlier this month, the Anthropocene Working Group, an international team of scientists, claimed they had found clear evidence of the beginning of the Anthropocene in a lake in Ontario, Canada. In the lake’s depths, sedimentary evidence was found of radioactive plutonium and hazardous fly ash from the burning of fossil fuels.
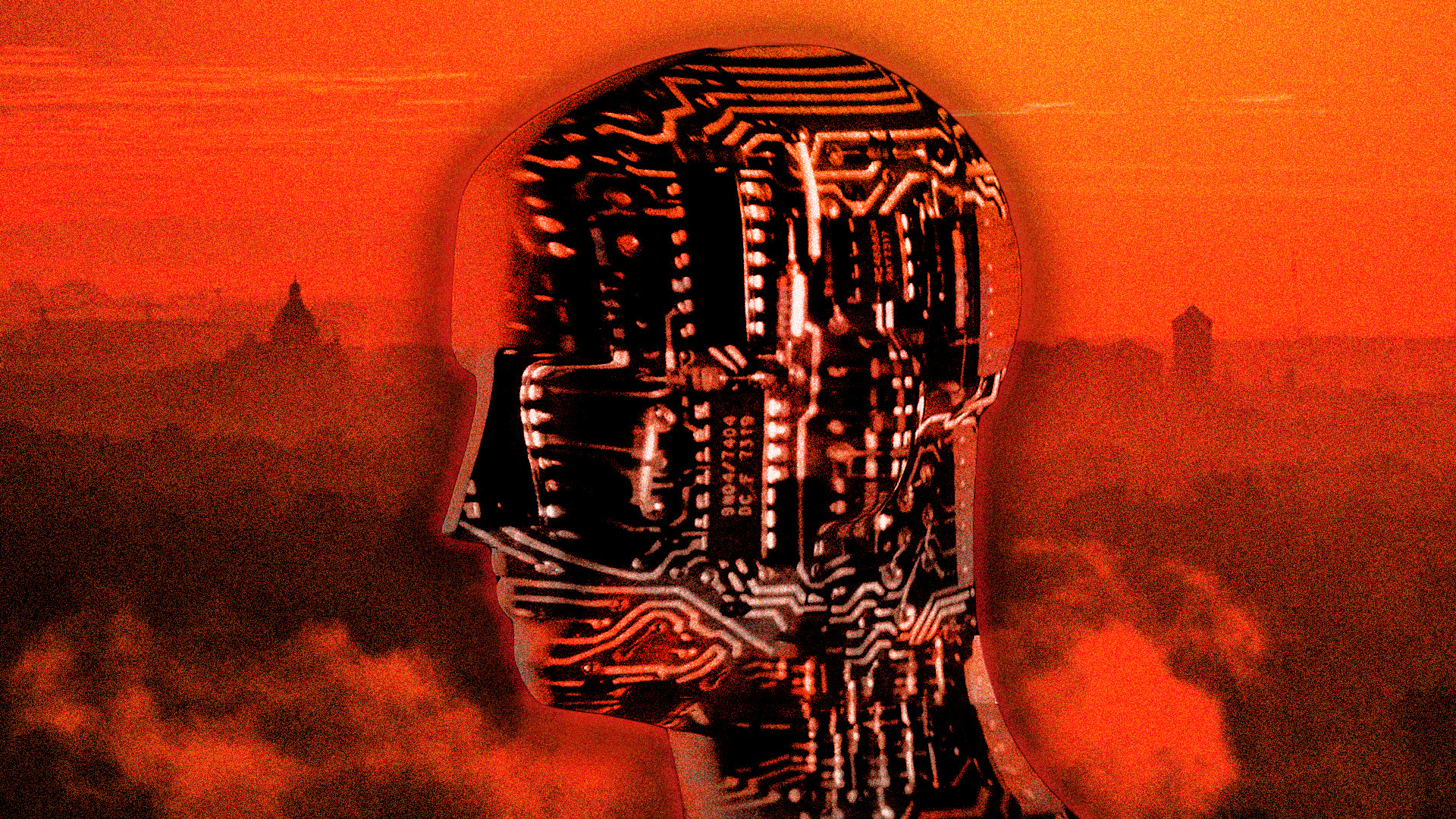
The havoc we have wreaked on our environment is why the Anthropocene epoch may be our last. Humanity has been talking about the apocalypse for thousands of years. But in 2023, as we grapple with the hottest temperatures ever recorded, the imminent threat of climate disaster and the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, there is a greater urgency to the questions some are asking about what the world would really look like without us. Would it be better to leave the Earth to the animals, to the trees, even to the rocks? And would the world be a safer and more benevolent place if we let AI robots run everything?
In “The Revolt Against Humanity: Imagining a Future Without Us,” the American poet and critic Adam Kirsch interrogates the prospect of a world that is no longer dominated by humans — either because we have driven ourselves to extinction or because we have been replaced by artificial intelligence. Sitting in a sweltering Rome on the hottest day ever recorded in the ancient capital, I spoke to Adam Kirsch on the phone in New York City, where the air quality index hovered near hazardous because of the wildfire smoke drifting over from Canada. It was difficult not to talk about the “end times.”
This conversation has been edited for length and clarity.
When did you first start thinking about a future without humans?
I began to want to write the book during the pandemic when, very quickly, I felt like my physical world contracted to the space of an apartment. It struck me how little of a difference that made to my life. So much of what I do and what most of us do can be done virtually rather than physically — whether it’s work, leisure or consumption. I began to think about the idea that human life has already changed. It has already gone virtual and disengaged from the physical in ways that our ancestors would not have understood. And the transhumanists’ idea is just another step on that path.
Let’s clarify for our readers what “transhumanists” think. They basically imagine a world where the human condition can be improved or even replaced by technology like AI, right?
Transhumanism is the school of thought which says that in the future, we will be able to use technology to overcome the limitations of our physical bodies. Transhumanists look to a future where humans will give way to another species or another form of life that isn’t embodied in flesh and blood. It isn’t necessarily mortal, and it might be able to live indefinitely, as a record of information, or as a simulation, or in the virtual world.
Or, alternatively, transhumanism says that we will just be able to escape the limitations of our bodies with genetic engineering. One of the most vivid strains of transhumanism right now is the idea that in a future with artificial intelligence, there might be minds that are not human minds at all. Minds that are actually born on computers and that have a very different relationship to reality and the physical world than we do. And that those minds will become the leading form of life on our planet and take over from us in a violent or benevolent way.
Another group you look at in your book also considers what the world would look like if humans no longer dominated it. They are called “anthropocene antihumanists” and seem to believe that humans are a kind of cancer on the earth, multiplying like a parasite. And that the world would be better off without us.
Antihumanists say that humans have taken over from nature as the most important factor on the planet. They say we no longer live alongside nature, but we control nature and dominate it. This, they believe, is eventually going to lead to the decline or disappearance of humanity itself. And they think that would be a good thing. So antihumanism can be anything from saying we should stop having children to predicting that an environmental calamity is going to reduce us to just a few leftover populations. Philosophically, it can take the form of saying, ‘How can we think about the world in ways that don’t put humanity at the center of it?’ They give equal respect and agency to nonhuman things and even nonliving things, like objects or the ocean.
Or a rock. It’s funny, I’ve been thinking a lot recently about what a world without humans looks like. Especially as I grapple with the realities of the climate crisis and biodiversity loss. I sometimes find myself fantasizing about what the natural world looked like before human civilization. Reading your book was an intense experience in that way, because it forces you to think about the Earth without humanity. What kind of place did it take you to psychologically, while you were writing?
It’s very difficult to imagine the disappearance of humanity as a real prospect — in the same way that it’s sort of hard to imagine what it’s like to be dead. We could all theoretically agree that at some point there will no longer be a human species, that we will have become extinct. And that just as the dinosaurs did, someday we will disappear. But to think about that happening tomorrow or next year plays havoc with all of our assumptions about what matters and how we go about our days. Thinking about these things is on a different track from daily life. In daily life, we’re dealing with the world as it is — raising children and going to work. We’re not thinking about the future in an abstract or philosophical way.
Yes, it’s a kind of bizarre cognitive dissonance to think about a world millions of years from now when humans don’t exist and then go back to thinking about what to have for lunch.
When the book was published in January, almost right away, all of the things that I was writing about started to become much more mainstream. First, there was ChatGPT, which led to people talking about artificial intelligence in a very immediate way and talking about how dangerous it might be. And then came this summer that we’re having with all these broken temperature records and parts of the world becoming dangerously hot and endangering human life. Even to me — someone who’s been thinking about this and researching and writing about it for a long time — when it erupts into your actual life, it seems like kind of a shock. We have a tendency to think about dire things or radical changes in the abstract and not deal with the concrete until we absolutely have to.
I think we rely so much on shards of hope that seem to get slimmer and slimmer every year. You talk about hope a lot in the book. How hopeful would you say you are?
I think that all of us rely on hope. We rely on the assumption that the future is going to be like the present because that’s the only way we know how to navigate the world. But one of the things that drew me to the people I write about in the book is that they’re not afraid to think about things that seem frightening or impossible, that most people dismiss as science fiction or extremism. They’re thinking through the idea of, ‘What if the world actually was like this in the future? What if we actually did have computers that could outthink us or what if billions of people could no longer survive because of climate change? What would that do to our sense of ourselves and the way we live?’ And I think that that’s useful to think about. Both for its own sake and because it maybe also makes us more willing to take action in the present.
There was one Franz Kafka quote in your book that really stood out to me. “There is hope — an infinite amount of hope — but not for us.” What does that mean to you?
What transhumanists and antihumanists are trying to say is, ‘Well, maybe in the future, there won’t be us, but there will be something else that we can be hopeful for.’ They say that the disappearance of humanity might not mean the end of everything that we care about. They’re trying to nudge us into a new way of thinking that if we’re not here, it might not matter that much — as long as something else is. Both of them think of humanity as a stage. That the normal progression of the human species is to supersede ourselves or eliminate ourselves, not by accident, but by necessity.
The story you just read is a small piece of a complex and an ever-changing storyline that Coda covers relentlessly and with singular focus. But we can’t do it without your help. Show your support for journalism that stays on the story by becoming a member today. Coda Story is a 501(c)3 U.S. non-profit. Your contribution to Coda Story is tax deductible.