Bauyrzhan Sabitov/The Village Kazakhstan
The smart city where everybody knows your name
- Photography by Bauyrzhan Sabitov
At first glance, Aqkol looks like most other villages in Kazakhstan today: shoddy construction, rusting metal gates and drab apartment blocks recall its Soviet past and lay bare the country’s uncertain economic future. But on the village’s outskirts, on a hill surrounded by pine trees, sits a large gray and white cube: a central nervous system connecting thousands of miles of fiber optic cables, sensors and data terminals that keeps tabs on the daily comings and goings of the village’s 13,000 inhabitants.
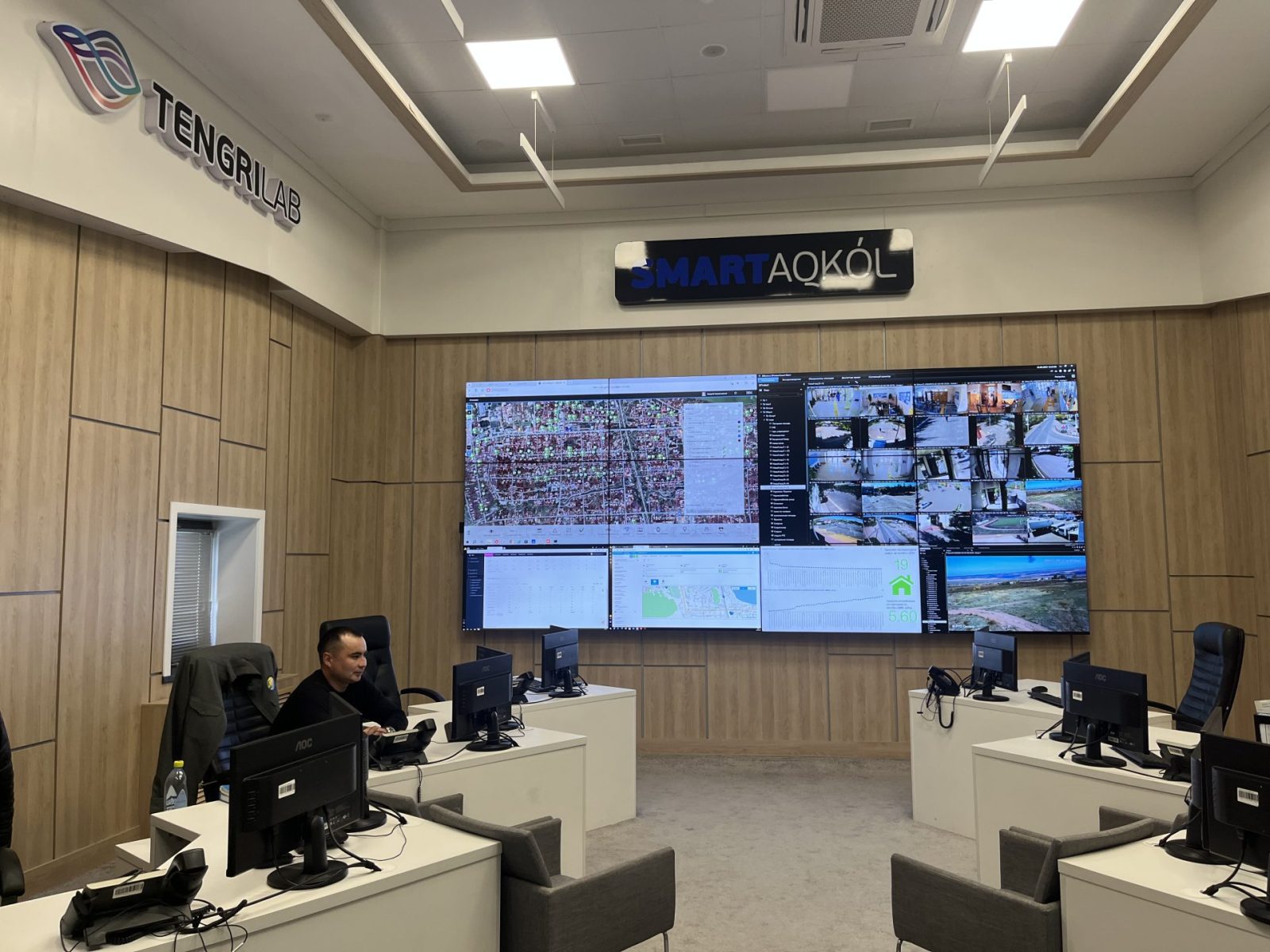
This is the command center of Smart Aqkol, a pilot study in digitized urban infrastructure for Kazakhstan. When I visited, Andrey Kirpichnikov, the deputy director of Smart Aqkol, welcomed me inside. Donning a black Fila tracksuit and sneakers, the middle-aged Aqkol native scanned his face at a console that bore the logo for Hikvision, the Chinese surveillance camera manufacturer. A turnstyle gave a green glow of approval and opened, allowing us to walk through.
“All of our staff can access the building using their unique face IDs,” Kirpichnikov told me.
He led me into a room with a large monitor displaying a schematic of the village. The data inputs and connected elements that make up Smart Aqkol draw on everything from solar panels and gas meters to GPS trackers on public service vehicles and surveillance cameras, he explained. Analysts at the command center report their findings to the mayor’s office, highlighting data on energy use, school attendance rates and evidence for police investigations.
“I see a huge future in what we’re doing here,” Kirpichnikov told me, gesturing at a heat map of the village on the big screen. “Our analytics keep improving and they are only going to get better as we expand the number of sensory inputs.”
“We’re trying to make life better, more efficient and safer,” he explained. “Who would be opposed to such a project?”

Smart Aqkol presents an experimental vision of Kazakhstan’s economic prospects and its technocratic leadership’s governing ambitions. In January 2019, when then-President Nursultan Nazarbayev spoke at the project’s launch, he waxed about a future in which public officials could use networked municipal systems to run Kazakhstan “like a company.” The smart city model is appealing for leaders of the oil-rich nation, which has struggled to modernize its economy and shed its reputation for rampant government corruption. But analysts I spoke with say it also marks a turn toward Chinese-style public surveillance systems. Amid the war in Ukraine, Kazakhstan’s engagement with China has deepened as a way to hedge against dependence on Russia, its former colonial patron.
Kazakhstan’s smart city initiatives aren’t starting from a digital zero. The country has made strides in digitizing public services, and now ranks second among countries of the former Soviet Union in the United Nations’ e-governance development index. (Estonia is number one.) The capital Astana also has established itself as a regional hub for fintech innovation.
And it’s not only government officials who want these systems. “There is a lot of domestic demand, not just from the state but also from Kazakhstan’s middle class,” said Erica Marat, a professor at the U.S. National Defense University. There’s an allure about smart city systems, which in China and other Asian cities are thought to have improved living standards and reduced crime.
They also hold some promise of increasing transparency around the work of public officials. “The government hopes that digital platforms can overcome cases of petty corruption,” said Oyuna Baldakova, a technology researcher at King’s College London. This would be a welcome shift for Kazakhstan, which currently ranks 101st out of 180 countries on Transparency International’s Corruption Perceptions Index.

But the pilot in Aqkol doesn’t quite align with these grander ambitions, at least not yet. Back at the command center, Kirpichnikov described how Aqkol saw a drop in violent crime and alcohol-related offenses after the system’s debut. But in a town of this size, where crime rates rarely exceed single digits, these kinds of shifts don’t say a whole lot.
As if to better prove the point, the team showed me videos of crime dramatizations that they recorded using the Smart Aqkol surveillance camera system. In the first video, one man lifted another off the ground in what was meant to mimic a violent assault, but looked much more like the iconic scene where Patrick Swayze lifts Jennifer Grey overhead at the end of “Dirty Dancing.” Another featured a man brandishing a Kalashnikov in one hand, while using the other to hold his cellphone to his ear. In each case, brightly colored circles and arrows appeared on the screen, highlighting “evidence” of wrongdoing that the cameras captured, like the lift and the Kalashnikov.
Kirpichnikov then led me into Smart Aqkol’s “situation room,” where 14 analysts sat facing a giant LED screen while they tracked various signals around town. Contrary to the high-stakes energy that one might expect in a smart city situation room, the atmosphere here felt more like that of a local pub, with the analysts trading gossip about neighbors as they watched them walk by on monitors for street-level cameras.


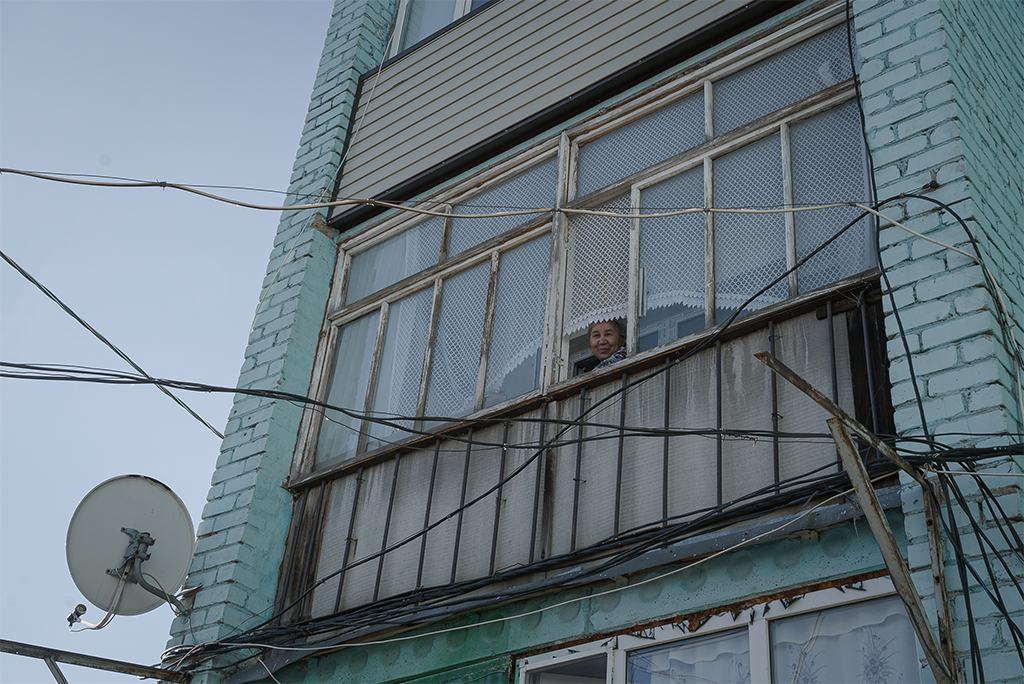
Kirpichnikov explained that residents can connect their gas meters to their bank accounts and set up automatic gas payments. This aspect of Smart Aqkol has been a boon for the village. Residents I spoke with praised the new payment system — for decades, the only option was to stand in line to pay for their bills, an exercise that could easily take half a day’s time.
And there was more. To highlight the benefits of Smart Aqkol’s analytics work, Kirpichnikov told me about recent finding: “We were able to determine that school attendance is lower among children from poorly insulated households.” He pointed to a gradation of purple squares showing variance in heating levels across the village. “We could improve school grades, health and the living standards of residents just by updating our old heating systems,” he said.
Kirpichnikov might be right, but step away from the clean digital interface and any Aqkol resident could tell you that poor insulation is a serious problem in the apartment blocks where most people live, especially in winter when temperatures dip below freezing most nights. Broken windows covered with only a thin sheet of cellophane are a common sight.
Walking around Aqkol, I was struck by the absence of paved roads and infrastructure beyond the village’s main street. Some street lamps work, but others don’t. And the public Wi-Fi that the village prides itself on offering only appeared to function near government buildings.

The village also has two so-called warm bus shelters — enclosed spaces with heat lamps to shelter waiting passengers during the harsh Kazakh winters. The stops are supposed to have Wi-Fi, charging ports for phones and single-channel TVs. When I passed by one of the shelters, I met an elderly Aqkol resident named Vera. “All of these things are gone,” she told me, waving her hand at evidence of vandalism. “Now all that’s left is the camera at the back.”
“I don’t know why we need all this nonsense here when we barely have roads and running water,” she added with a sigh. “Technology doesn’t make better people.”
Vera isn’t alone in her critique. Smart Aqkol has brought the village an elaborate overlay of digitization, but it’s plain to see that Aqkol still lags far behind modern Kazakh cities like Astana and Almaty when it comes to basic infrastructure. A local resident named Lyubov Gnativa runs a YouTube channel where she talks about Aqkol’s lack of public services and officials’ failures to address these needs. The local government has filed police reports against Gnativa over the years, accusing her of misleading the public.
And a recent documentary made by Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty — titled “I Love My Town, But There’s Nothing Smart About It” — corroborates many of Gnativa’s observations and includes interviews with with dozens of locals drawing attention to water issues and the lack of insulation in many of the village’s homes.
But some residents say they are grateful for how the system has contributed to public safety. Surveillance cameras now monitor the village’s main thoroughfare from lampposts, as well as inside public schools, hospitals and municipal buildings.
“These cameras change the way people behave and I think that’s a good thing,” said Kirpichnikov. He told a story about a local woman who was recently harassed on a public bench, noting that this kind of interaction would often escalate in the past. “The woman pointed at the camera and the man looked up, got scared and began to walk away.”
A middle-aged schoolteacher named Irina told me she feels much safer since the project was implemented in 2019. “I have to walk through a public park at night and it can be intimidating because a lot of young men gather there,” she said. “After the cameras were installed they never troubled me again.”

The Smart Aqkol project was the result of a deal between Kazakhtelecom, Kazakhstan’s national telecommunications company; the Eurasian Resources Group, a state-backed mining company; and Tengri Lab, a tech startup based in Astana. But the hardware came through an agreement under China’s Digital Silk Road initiative, which seeks to wire the world in a way that tends to reflect China’s priorities when it comes to public infrastructure and social control. Smart Aqkol uses surveillance cameras made by Chinese firms Dahua and Hikvision, which in China have been used — and touted, even — for their ability to track “suspicious” people and groups. Both companies are sanctioned by the U.S. due to their involvement in surveilling and aiding in the repression of ethnic Uyghurs in Xinjiang, an autonomous region in western China.
Critics are wary of these kinds of systems in Kazakhstan, where skepticism of China’s intentions in Central Asia has been growing. The country is home to a large Uyghur diaspora of more than 300,000 people, many of whom have deep ties to Xinjiang, where both ethnic Uyghurs and ethnic Kazakhs have been systematically targeted and placed in “re-education” camps. Protests across Kazakhstan in response to China’s mass internment campaign have forced the government to negotiate the release of thousands of ethnic Kazakhs from China, but state authorities have walked this line carefully, in an effort to continue expanding economic ties with Beijing.
Although Kazakhstan requires people to get state permission if they want to hold a protest — and permission is regularly denied — demonstrations nevertheless have become increasingly common in Kazakhstan since 2018. With Chinese-made surveillance tech in hand, it’s become easier than ever for Kazakh authorities to pinpoint unauthorized concentrations of people. Hikvision announced in December 2022 that its software is used by Chinese police to set up “alarms” that are triggered when cameras detect “unlawful gatherings” in public spaces. The company also has claimed that its cameras can detect ethnic minorities based on their unique facial features.

Marat of U.S. National Defense University noted the broader challenges posed by surveillance tech. “We saw during the Covid-19 pandemic how quickly such tech can be adapted to other purposes such as enforcing lockdowns and tracing people’s whereabouts.”
“Such technology could easily be used against protest leaders too,” she added.
In January 2022, instability triggered by rising energy prices resulted in the government issuing “shoot to kill” orders against protesters — more than 200 people were killed in the ensuing clashes. The human rights news and advocacy outlet Bitter Winter wrote at the time that China had sent a video analytics team to Kazakhstan to use cameras it had supplied to identify and arrest protesters. Anonymous sources in their report alleged that the facial profiles of slain protesters were later compared with the facial data of individuals who appeared in surveillance video footage of riots, in an effort to justify government killings of “terrorists.”
With security forming a central promise of the smart city model, broad public surveillance is all but guaranteed. The head of Tengri Lab, the company leading the development of Smart Aqkol, has said in past interviews that school security was a key motivation behind the company’s decision to spearhead the use of artificial intelligence-powered cameras.
“After the high-profile incident in Kerch, we added the ability to automatically detect weapons,” he said, referencing a mass shooting at a college in Russian-occupied Crimea that left more than 20 people dead in October 2018. In that same speech he made an additional claim: “All video cameras in the city automatically detect massive clusters of people,” a veiled reference to the potential for this technology to be used against protesters.
Soon, there will be more smart city systems across Kazakhstan. Smart Aqkol and Kazakhtelecom have signed memorandums of understanding with Almaty, home to almost 2 million people, and Karaganda, with half a million, to develop similar systems. “The mayor of Karaganda was impressed by our technology and capabilities, but he was mainly interested in the surveillance cameras,” Kirpichnikov told me.
As to the question of whether these systems share data with Chinese officials, “we simply don’t have a clear answer on who has the data and how it is used,” Marat told me. “We can’t say definitively whether China has access but we know its companies are extremely dependent on the Chinese state.”
When I reached out to Tengri Lab to ask whether there are concerns regarding the safety of private data connected to the project, the company declined to comment.

What does all this mean for Aqkol? The village is so small that the faces captured on camera are rarely those of strangers. The analysts told me they recognize most of the town’s 13,000 inhabitants between them. I asked whether this makes people uncomfortable, knowing their neighbors are watching them at all times.
Danir, a born-and-raised Aqkol analyst in the situation room, told me he doesn’t believe the platform will be abused. “All my friends and family know I am watching from this room and keeping them safe,” he said. “I don’t think anybody feels threatened — we are their friends, their neighbors.”
“People fear what they don’t understand and people complain about the cameras until they need them,” said Kirpichnikov. “There was a woman once who spoke publicly against the project but after we returned her lost handbag — after we spotted it on a camera — she started to see the benefits of what we are building here.”
After a few years with the system up and running, “it’s normal,” said Danir with a shrug. “Nobody has complained to me.”
For regular people, it doesn’t mean a whole lot. And that may be OK, at least for now. As Irina, the young school teacher whom I met on the village’s main thoroughfare, put it: “I don’t really know what a smart city is, but I like living here. They say we’re safer and my bills are lower than they used to be, and I’m happy.”
The story you just read is a small piece of a complex and an ever-changing storyline that Coda covers relentlessly and with singular focus. But we can’t do it without your help. Show your support for journalism that stays on the story by becoming a member today. Coda Story is a 501(c)3 U.S. non-profit. Your contribution to Coda Story is tax deductible.