The Indian migrants lured into forced labor on Mussolini’s farmland
Gurinder Dhillon still remembers the day he realized he had been tricked. It was 2009, and he had just taken out a $16,000 loan to start a new life. Originally from Punjab, India, Dhillon had met an agent in his home village who promised him the world.
“He sold me this dream,” Dhillon, 45, said. A new life in Europe. Good money — enough to send back to his family in India. Clothes, a house, plenty of work. He’d work on a farm, picking fruits and vegetables, in a place called the Pontine Marshes, a vast area of farmland in the Lazio region, south of Rome, Italy.
He took out a sizable loan from the Indian agents, who in return organized his visa, ticket and travel to Italy. The real cost of this is around $2,000 — the agents were making an enormous profit.
“The thing is, when I got here, the whole situation changed. They played me,” Dhillon said. “They brought me here like a slave.”

On his first day out in the fields, Dhillon climbed into a trailer with about 60 other people and was then dropped off in his assigned hoop house. That day, he was on the detail for zucchini, tomatoes and eggplant. It was June, and under the plastic, it was infernally hot. It felt like at least 100 degrees, Dhillon remembers. He sweated so much that his socks were soaked. He had to wring them out halfway through the day and then put them back on — there was no time to change his clothes. As they worked, an Italian boss yelled at them constantly to work faster and pick more.
Within a few hours of that first shift, it dawned on Dhillon that he had been duped. “I didn’t think I had been tricked — I knew I had,” he said. This wasn’t the life or the work he had been promised.
What he got instead was 3.40 euros (about $3.65) an hour, for a workday of up to 14 hours. The workers weren’t allowed bathroom breaks.
On these wages, he couldn’t see how he would ever repay the enormous loan he had taken out. He was working alongside some other men, also from India, who had been there for years. ”Will it be like this forever?” he asked them. “Yes,” they said. “It will be like this forever.”

Ninety years ago, a very different harvest was taking place. Benito Mussolini was celebrating the first successful wheat harvest of the Pontine Marshes. It was a new tradition for the area, which for millennia had been nothing but a vast, brackish, barely-inhabited swamp.
No one managed to tame it — until Mussolini came to power and launched his “Battle for Grain.” The fascist leader had a dream for the area: It would provide food and sustenance for the whole country.
Determined to make the country self-sufficient as a food producer, Mussolini spoke of “freeing Italy from the slavery of foreign bread” and promoted the virtues of rural land workers. At the center of his policy was a plan to transform wild, uncultivated areas into farmland. He created a national project to drain Italy’s swamps. And the boggy, mosquito-infested Pontine Marshes were his highest priority.
His regime shipped in thousands of workers from all over Italy to drain the waterlogged land by building a massive system of pumps and canals. Billions of gallons of water were dredged from the marshes, transforming them into fertile farmland.
The project bore real fruit in 1933. Thousands of black-shirted Fascists gathered to hear a brawny-armed, suntanned Mussolini mark the first wheat harvest of the Pontine Marshes.
"The Italian people will have the necessary bread to live,” Il Duce told the crowd, declaring how Italy would never again be reliant on other countries for food. “Comrade farmers, the harvest begins.”
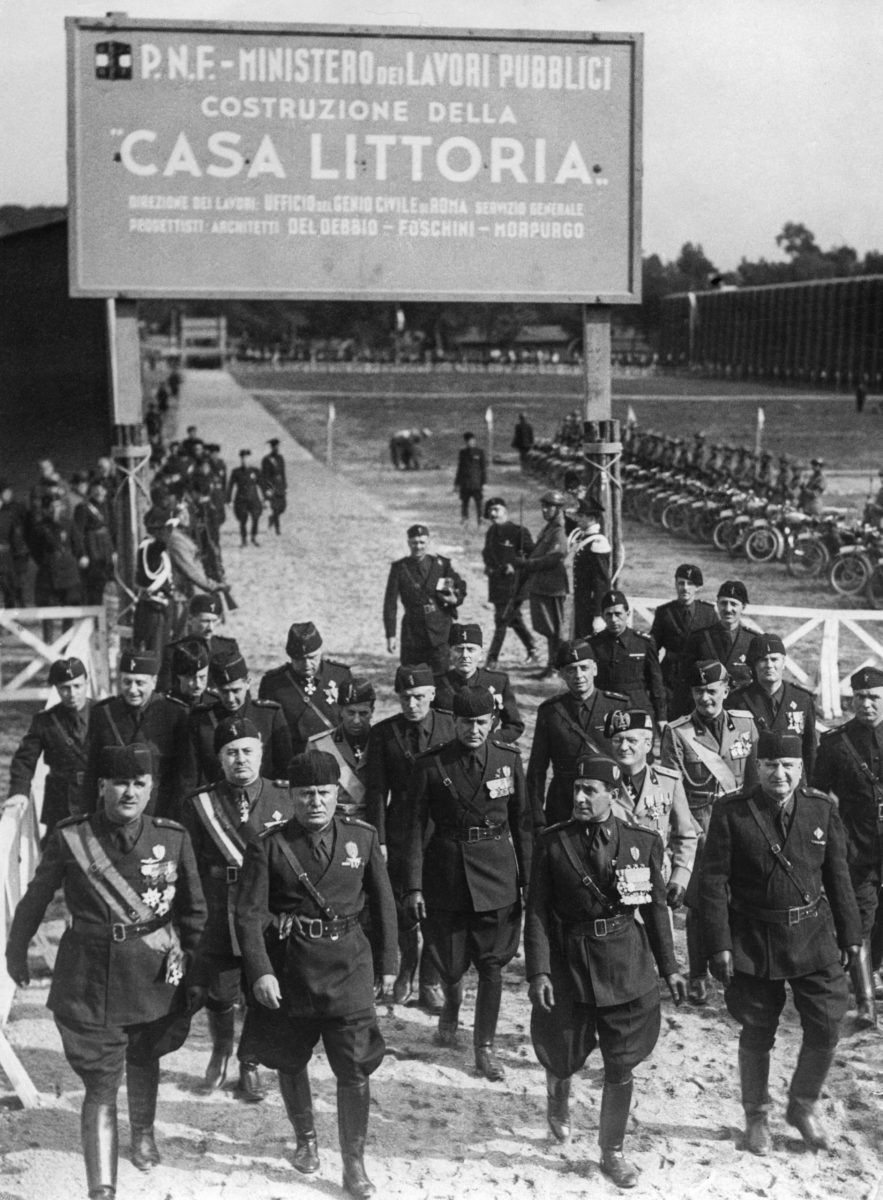
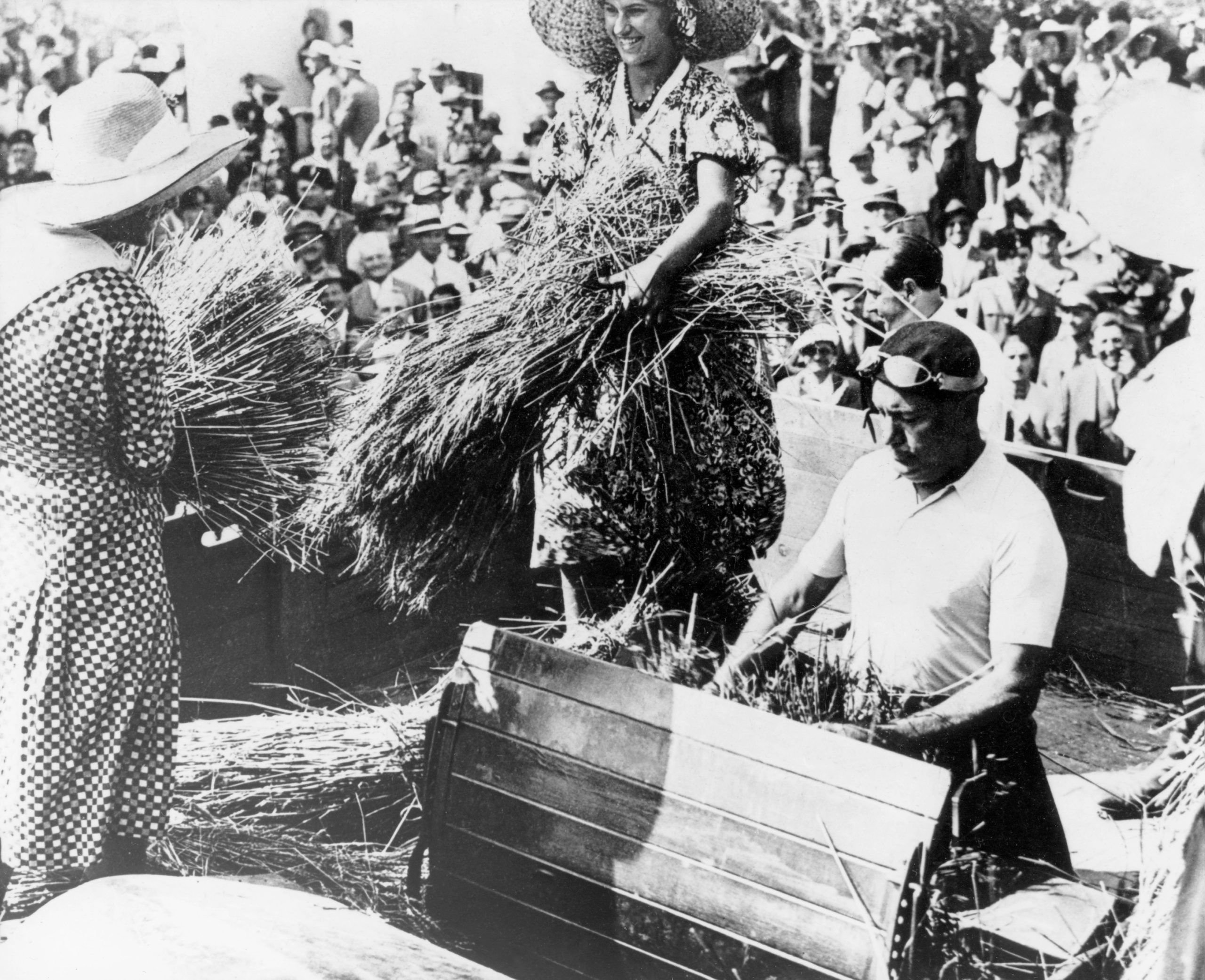



Bettmann / Contributor / Getty Images.
The Pontine Marshes are still one of the most productive areas of Italy, an agricultural powerhouse with miles of plastic-covered hoop houses, growing fruit and vegetables by the ton. They are also home to herds of buffalo that make Italy’s famous buffalo mozzarella. The area provides food not just for Italy but for Europe and beyond. Jars of artichokes packed in oil, cans of Italian plum tomatoes and plump, ripe kiwi fruits often come from this part of the world. But Mussolini’s “comrade farmers” harvesting the land’s bounty are long gone. Tending the fields today are an estimated 30,000 agricultural workers like Dhillon, most hailing from Punjab, India. For many of them — and by U.N. standards — the working conditions are akin to slave labor.
When Urmila Bhoola, the U.N. special rapporteur on contemporary slavery, visited the area, she found that many working conditions in Italy’s agricultural sector amounted to forced labor due to the amount of hours people work, the low salaries and the gangmasters, or “caporali,” who control them.
The workers here are at the mercy of the caporali, who are the intermediaries between the farm workers and the owners. Some workers are brought here with residency and permits, while others are brought fully off the books. Regardless, they report making as little as 3-4 euros an hour. Sometimes, though, they’re barely paid at all. When Samrath, 34, arrived in Italy, he was not paid for three months of work on the farms. His boss claimed his pay had gone entirely into taxes — but when he checked with the government office, he found his taxes hadn’t been paid either.
Samrath is not the worker’s real name. Some names in this story have been changed to protect the subjects’ safety.
“I worked for him for all these months, and he didn’t pay me. Nothing. I worked for free for at least three months,” Samrath told me. “I felt so ashamed and sad. I cried so much.” He could hardly bring himself to tell his family at home what had happened.



I met Samrath and several other workers on a Sunday on the marshes. For the Indian Sikh workers from Punjab, this is usually the only day off for the week. They all gather at the temple, where they pray together and share a meal of pakoras, vegetable curry and rice. The women sit on one side, the men on the other. It’s been a long working week — for the men, out in the fields or tending the buffaloes, while the women mostly work in the enormous packing centers, boxing up fruits and vegetables to be sent out all over Europe.
Another worker, Ramneet, told me how he waited for his monthly check — usually around 1,300 euros (about $1,280) per month, for six days’ work a week at 12-14 hours per day. But when the check came, the number on it was just 125 euros (about $250).
“We were just in shock,” Ramneet said. “We panicked — our monthly rent here is 600 euros.” His boss claimed, again, that the money had gone to taxes. It meant he had worked almost for free the entire month. Other workers explained to me that even when they did have papers, they could risk being pushed out of the system and becoming undocumented if their bosses refused to issue them payslips.
Ramneet described how Italian workers on the farms are treated differently from Indian workers. Italian workers, he said, get to take an hour for lunch. Indian workers are called back after just 20 minutes — despite having their pay cut for their lunch hour.
“When Meloni gives her speeches, she talks about getting more for the Italians,” Ramneet’s wife Ishleen said, referring to Italy’s new prime minister and her motto, “Italy and Italians first.” “She doesn’t care about us, even though we’re paying taxes. When we’re working, we can’t even take a five-minute pause, while the Italian workers can take an hour.”
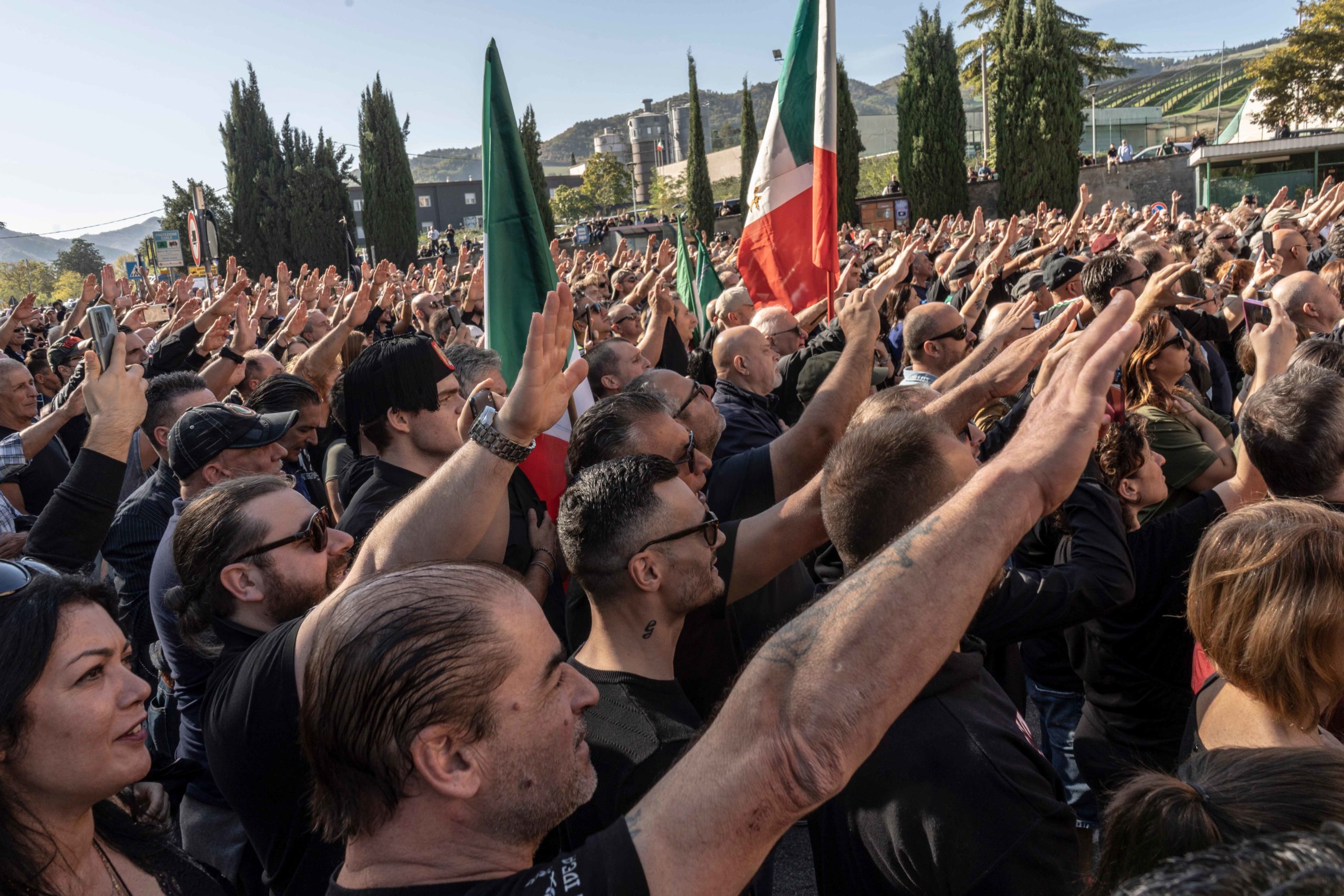


Today, Italy is entering a new era — or, some people argue, returning to an old one. In September, Italians voted in a new prime minister, Giorgia Meloni. As well as being the country’s first-ever female prime minister, she is also Italy’s most far-right leader since Mussolini. Her supporters — and even some leaders of her party, Brothers of Italy — show a distinct reverence for Mussolini’s National Fascist Party.
In the first weeks of Meloni’s premiership, thousands of Mussolini admirers made a pilgrimage to Il Duce’s birthplace of Predappio to pay homage to the fascist leader, making the Roman salute and hailing Meloni as a leader who might resurrect the days of fascism. In Latina, the largest city in the marshes, locals interviewed by national newspapers talked of being excited about Meloni’s victory — filled with hopes that she might be true to her word and bring the area back to its glory days in the time of Benito Mussolini. One of Meloni’s undersecretaries has run a campaign calling for a park in Latina to return to its original name: Mussolini Park.
During her campaign, a video emerged of Meloni discussing Mussolini as a 19-year-old activist. “I think Mussolini was a good politician. Everything he did, he did for Italy,” she told journalists. Meloni has since worked to distance herself from such associations with fascism. In December, she visited Rome’s Jewish ghetto as a way of acknowledging Mussolini’s crimes against humanity. “The racial laws were a disgrace,” she told the crowd.
A century on from Italy’s fascist takeover, Meloni’s victory has led to a moment of widespread collective reckoning, as a national conversation takes place about how Mussolini should be remembered and whether Meloni’s premiership means Italy is reconnecting with its fascist past.
Unlike in Germany, which tore down — and outlawed — symbols of Nazi terror, reminders of Mussolini’s rule remain all over Italy. There was no moment of national reckoning after the war ended and Mussolini was executed. Hundreds of fascist monuments and statues dot the country. Slogans left over from the dictatorship can be seen on post offices, municipal buildings and street signs. Collectively, when Italians discuss Mussolini, they do remember his legacy of terror — his alliance with Adolf Hitler, anti-Semitic race laws and the thousands of Italian Jews he sent to the death camps. But across the generations, Italians also talk about other legacies of his regime — they talk of the infrastructure and architecture built during the period and of how he drained the Pontine Marshes and rid them of malaria, making the land into an agricultural haven.
Today in the Pontine Marshes, which some see as a place brought into existence by Il Duce — and where the slogans on one town tower praise “the land that Mussolini redeemed from deadly sterility” — the past is bristling with the present.
“The legend that has come back to haunt this town, again and again, is that it’s a fascist city. Of course, it was created in the fascist era, but here we’re not fascists — we’re dismissed as fascists and politically sidelined as a result,” Emilio Andreoli, an author who was born in Latina and has written books about the city’s history, said. Politicians used to target the area as a key campaigning territory, he said, but it has since fallen off most leaders’ agendas. And indeed, in some ways, Latina is a place that feels forgotten. Although it remains a top agricultural producer, other kinds of industry and infrastructure have faltered. Factories that once bustled here lie empty. New, faster roads and railways that were promised to the city by previous governments never materialized.


Meloni did visit Latina on her campaign trail and gave speeches about reinvigorating the area with its old strength. “This is a land where you can breathe patriotism. Where you breathe the fundamental and traditional values that we continue to defend — despite being considered politically incorrect,” she told the crowd.
But the people working this land are entirely absent from Meloni’s rhetorical vision. Marco Omizzolo, a professor of sociology at the University of Sapienza in Rome, has for years studied and engaged with the largely Sikh community of laborers from India who work on the marshes.
Omizzolo explained to me how agricultural production in Italy has systematically relied on the exploitation of migrant workers for decades.
“Many people are in this,” he told me, when we met for coffee in Rome. “The owners of companies who employ the workers. The people who run the laborers’ daily work. Local and national politicians. Several mafia clans.”
“Exploitation in the agricultural sector has been going on for centuries in Italy,” Giulia Tranchina, a researcher at Human Rights Watch focusing on migration, said. She described that the Italian peasantry was always exploited but that the system was further entrenched with the arrival of migrant workers. “The system has always treated migrants as manpower — as laborers to exploit, and never as persons carrying equal rights as Italian workers.” From where she’s sitting, Italy’s immigration laws appear to have been designed to leave migrants “dependent on the whims and the wills of their abusive employers,” Tranchina said.
The system of bringing the workers to Italy — and keeping them there — begins in Punjab, India. Omizzolo described how a group of traffickers recruits prospective workers with promises of lucrative work abroad and often helps to arrange high-interest loans like the one that Gurinder took out. Omizzolo estimates that about a fifth of the Indian workers in the Pontine Marshes come via irregular routes, with some arriving from Libya, while many others are smuggled into Italy from Serbia across land and sea, aided by traffickers. Their situation is more perilous than those who arrived with visas and work permits, as they’re forced to work under the table without contracts, benefits or employment rights.
Omizzolo knows it all firsthand. A Latina native, he grew up playing football by the vegetable and fruit fields and watching as migrant workers, first from North Africa, then from India, came to the area to work the land. He began studying the forces at play as a sociologist during his doctorate and even traveled undercover to Punjab to understand how workers are picked up and trafficked to Italy.
As a scholar and advocate for stronger labor protections, he has drawn considerable attention to the exploitative systems that dominate the area. In 2016, he worked alongside Sikh laborers to organize a mass strike in Latina, in which 4,000 people participated. All this has made Omizzolo a target of local mafia forces, Indian traffickers and corrupt farm bosses. He has been surveilled and chased in the street and has had his car tires slashed. Death threats are nothing unusual. These days, he does not travel to Latina without police protection.

The entire system could become even further entrenched — and more dangerous for anyone speaking out about it — under Meloni’s administration. The prime minister has an aggressively anti-migrant agenda, promising to stop people arriving on Italy’s shores in small boats. Her government has sent out a new fleet of patrol boats to the Libyan Coast Guard to try to block the crossings, while making it harder for NGOs to carry out rescue operations.
At the end of February, at least 86 migrants drowned off the coast of Calabria in a shipwreck. When Meloni visited Calabria a few weeks later, she did not go to the beach where the migrants’ bodies were found or to the funeral home that took care of their remains. Instead, she announced a new policy: scrapping special protection residency permits for migrants.
Subscribe to our Authoritarian Tech newsletter
From biometrics to surveillance — when people in power abuse technology, the rest of us suffer. Written by Ellery Biddle.
Tranchina, from Human Rights Watch, explained that getting rid of the “special protection” permits will leave many migrant workers in Italy, including those in the Pontine Marshes, effectively undocumented.
“The situation is worsening significantly under the current government,” she said. “An army of people, who are currently working, paying taxes, renting houses, will now be forced to accept very exploitative working conditions — at times akin to slavery — out of desperation.”
Omizzolo agreed. Meloni’s hostile environment campaign against arriving migrants is making people in the marshes feel “more fragile and blackmailable,” he told me.
“Meloni is entrenching the current system in place in the Pontine Marshes,” Omizzolo said. “Her policies are interested in keeping things in their current state. Because the people who exploit the workers here are among her voter base.”
And then there’s the matter of money and how people are paid. A few months into her administration, Meloni introduced a proposal to raise the ceiling for cash transactions from 2,000 euros (about $2,110) to 5,000 euros ($5,280), a move that critics saw as an attempt to better insulate black market and organized crime networks from state scrutiny.
Workers describe that they were often paid in cash and that their bosses were always looking for ways to take them off the books. “We have to push them to pay us the official way and keep our contracts,” Rajvinder, 24, said. “They prefer to give us cash.” Being taken off a contract and paid under the table is a constant source of anxiety. “If I don’t have a work contract, my papers will expire after three months,” Samrath explained, describing how he would then become undocumented in Italy.
Omizzolo says Meloni’s cash laws will continue to preserve the corruption and sustain a shadow economy that grips the workers coming to the Pontine Marshes. Even for people who once worked above the table, the new government’s laissez-faire attitude towards the shadow economy is pushing them back into obscurity. “That law is directly contributing to the black market — people who used to be on the books, and have proper contracts, are now re-entering the shadow economy,” he said.
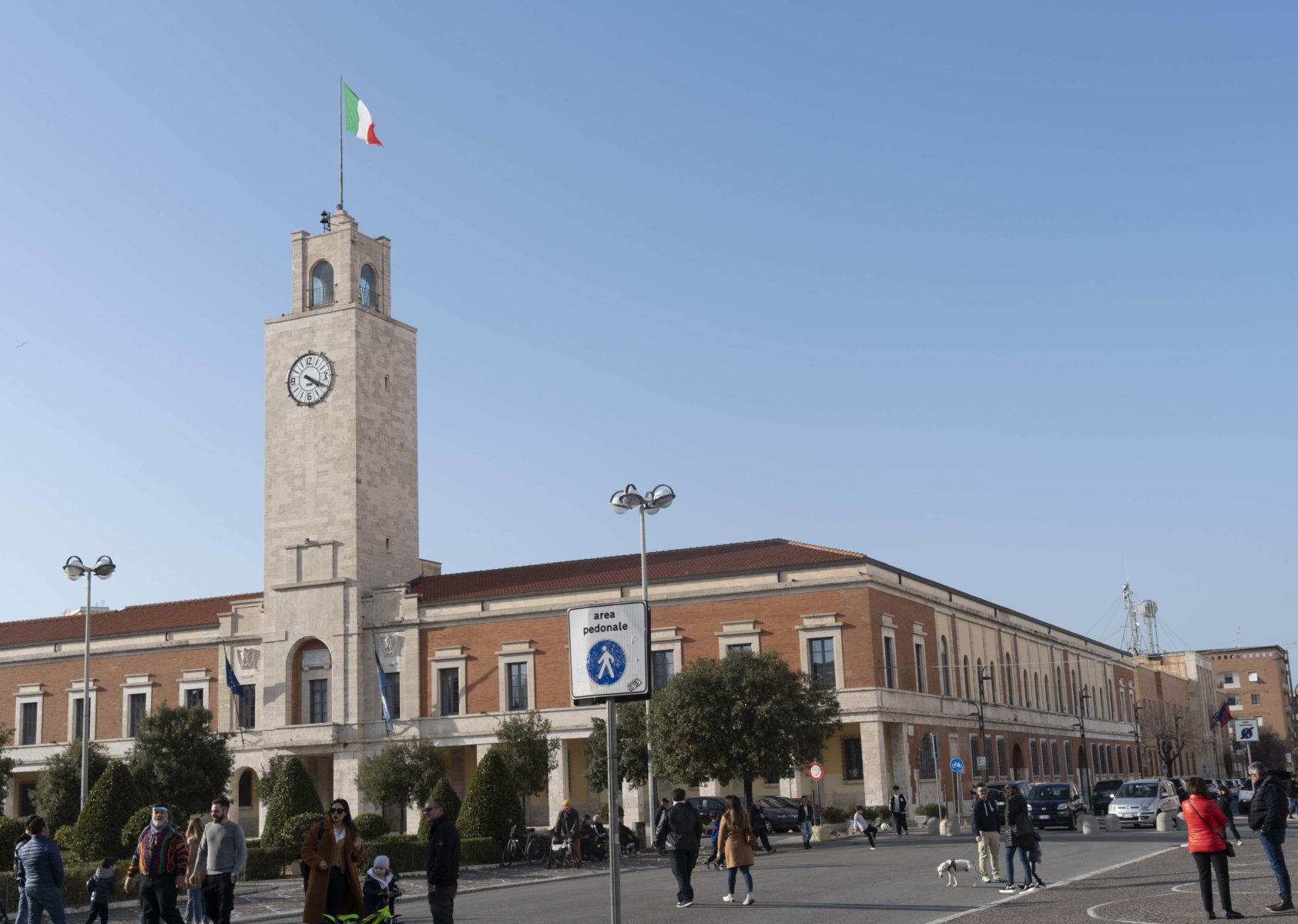

In December, Latina celebrated its 90th anniversary — some people here call it the youngest city in Italy. Some believe that this land, with its marble towns built in the fascist rationalist style, has fascism and Mussolini to thank for its very existence. The town was founded as a kind of utopia: a vision for a fascist future.
“This place was born in 1932. You can see it everywhere, in the architecture, in the buildings. We can’t skip over fascism. We can’t tell this story from the beginning while cutting things away to suit our convenience,” Cesare Bruni, who organizes a monthly “market of memory” where people sell antiques and relics from the past, said.
Bruni holds up an old photo from the New York Sunday News, showing a sun-dappled Mussolini visiting the newly drained marsh to help with the first harvest since the land was reclaimed, wearing a wide-brimmed hat. “Il Duce-Farmhand,” the headline reads, describing how the leader “put in three hours of hard work” out in the fields.


The idealistic image of the harvest was powerful propaganda at the time. Not shown were the workers, brought in from all over the country, who died of malaria while digging the trenches and canals to drain the marsh. It also stands in contrast to today’s reality. Workers are brought here from the other side of the world, on false pretenses, and find themselves trapped in a system with no escape from the brutal work schedule and the resulting physical and mental health risks. In October, a 24-year-old Punjabi farm worker in the town of Sabaudia killed himself. It’s not the first time a worker has died by suicide — depression and opioid addiction are common among the workforce.
“We are all guilty, without exception. We have decided to lose this battle for democracy. Dear Jaspreet, forgive us. Or perhaps, better, haunt our consciences forever,” Omizzolo wrote on his Facebook page.
Talwinder, 28, arrived on the marsh last year. “I had no hopes in India. I had no dreams, I had nothing. It is difficult here — in India, it was difficult in a different way. But at least [in India] I was working for myself.” His busiest months of the year are coming up — he’ll work without a day off. And although the mosquitoes no longer carry malaria, they still plague the workers. “They’re fatter than the ones in India,” he laughs. “I heard it’s because this place used to be a jungle.”
Mussolini’s vision for the marsh was to turn it into an agricultural center for the whole of Italy, giving work to thousands of Italians and building up a strong working peasantry. Today, vegetables, olives and cheeses from the area are shipped to the United States and sold in upmarket stores to shoppers seeking authentic, artisan foods from the heart of the old world. But it comes at an enormous price to those who produce it. And under Meloni’s premiership, they only expect that cost to rise.
“These days, if my family ask me if they should come here, like my nephew or relatives, I tell them no,” said Samrath. “Don’t come here. Stay where you are.”
The story you just read is a small piece of a complex and an ever-changing storyline that Coda covers relentlessly and with singular focus. But we can’t do it without your help. Show your support for journalism that stays on the story by becoming a member today. Coda Story is a 501(c)3 U.S. non-profit. Your contribution to Coda Story is tax deductible.
The Big Idea
Shifting Borders
-

When your body becomes the border
feature Erica Hellerstein
-

India and China draw a line in the snow
feature Shougat Dasgupta
-

How an EU-funded agency is working to keep migrants from reaching Europe
feature Zach Campbell and Lorenzo D'Agostino
-

Turkey uses journalists to silence critics in exile
feature Frankie Vetch